Summary
-
Fatigue causes 13%+ of workplace injuries and impairs critical safety functions.
-
Shift work and long hours are major contributors to fatigue-related incidents.
-
Readi enables proactive fatigue management—without cameras or wearables.
-
Organizations using Readi have cut alarm fatigue and improved operational safety.
Fatigue: The Silent Threat to Workplace Safety
Fatigue is a hidden danger in many operations. It slows reaction times, impairs memory, and increases the likelihood of errors. When ignored, it leads to near misses—or worse.
13% of all workplace injuries are fatigue-related (National Safety Council), and workers sleeping under 6 hours are 70% more likely to have an accident.
If your operation relies on night shifts, long hours, or 24/7 staffing, this issue affects you.
| Statistic | Source |
|---|---|
| 13% of workplace injuries involve fatigue | NSC |
| Night shift workers have 2x the injury risk | NIOSH |
| Fatigue impairs reaction time like alcohol | Journal of Sleep Research |
| Only 43% of employers train on fatigue | NSC Fatigue SurveyWhy Shift Work Makes It Worse |
Shift workers often deal with:
-
Disrupted circadian rhythms
-
Shortened or poor-quality sleep
-
Compounded fatigue across consecutive shifts
Microsleeps, memory lapses, and poor judgment are common results—especially without rest recovery.
Why Shift Work and Fatigue Are a Dangerous Combo
Shift work, especially night shifts or extended hours, can disrupt circadian rhythms and reduce total sleep duration. Over time, this leads to chronic fatigue that goes unnoticed until a near-miss or serious injury occurs.
Employees in these roles often experience:
-
Microsleeps on the job
-
Poor sleep recovery between shifts
-
Compounded fatigue over multiple days
-
Increased risk of long-term health problems
This makes fatigue risk assessment essential, not optional.
Notable Workplace Accidents Caused by Fatigue
Real-world examples underscore the devastating impact of fatigue on safety:
-
Exxon Valdez Oil Spill (1989)
Investigators cited crew fatigue as a major contributing factor. Sleep-deprived officers failed to properly maneuver the vessel, leading to one of the worst environmental disasters in history. -
BP Texas City Refinery Explosion (2005)
Fatigue among operators and inadequate shift change procedures were contributing factors in the explosion that killed 15 workers and injured over 180. -
Metro-North Train Derailment (2013)
The engineer fell asleep at the controls due to undiagnosed sleep apnea. Four passengers died, and over 60 were injured. Investigators tied the accident to sleep-related fatigue. -
Colgan Air Flight 3407 Crash (2009)
Fatigue was cited as a likely contributor in the crash that killed 50 people. The pilots had logged long travel hours and insufficient rest before the flight. -
Shell Offshore Drilling Rig Incident (2014)
Fatigue-related errors contributed to a blowout preventer test failure. The operator had been awake for 20 hours, highlighting risks in offshore shift environments.
These incidents demonstrate that fatigue doesn’t just reduce productivity—it can destroy lives, reputations, and operations. Proactive systems like Readi are critical to identifying fatigue risk early and preventing such outcomes.
From Reactive to Predictive: Enter Readi
Traditional reactive fatigue management tools only act after fatigue sets in (e.g. fatigue alarms, camera systems). But Readi offers a smarter, predictive approach.
What is Readi?
Readi is a predictive fatigue management platform that:
-
Forecasts fatigue risk up to 30 days ahead
-
Doesn’t require wearables or cameras (although the ReadiWatch is available)
-
Integrates into dispatcher or supervisor workflows
-
Is union-approved and privacy-compliant, as it doesn't require sleep tracking to predict fatigue
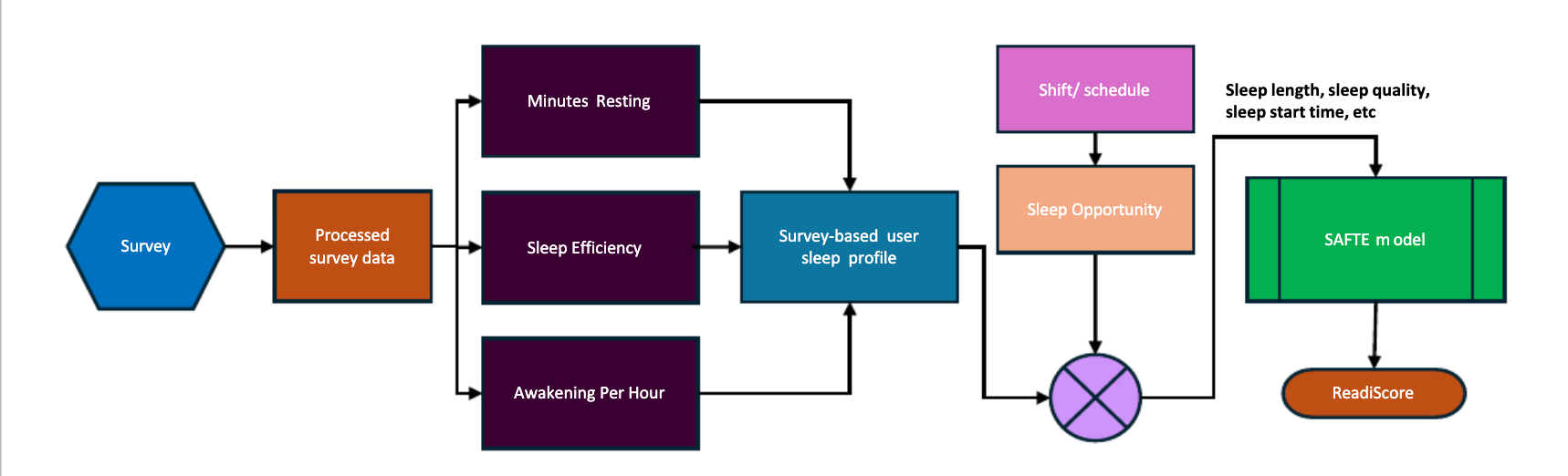
By using schedule and sleep pattern data, Readi helps teams take proactive action—like shift changes or task adjustments—before accidents happen.
Traditional vs Predictive Fatigue Tools
| Feature | Fatigue Alarms / Cameras | Readi Predictive Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | After symptoms appear | Before symptoms emerge |
| Privacy | High risk (surveillance) | Low risk (no monitoring) |
| Setup Effort | Hardware installation | Software or hardware options |
| Alarm Fatigue Risk | High | Reduced up to 58% |
| Works for All Shift Types and Environments | No | Yes |
How to Prevent Fatigue-Related Accidents
-
Use predictive fatigue risk assessment
Platforms like Readi identify who’s at risk, when, and why to allow for proactive action.
Download our list of fatigue countermeasures for dispatchers and supervisors. -
Improve scheduling practices
Avoid stacking night shifts or excessively long shifts without breaks. -
Train teams on fatigue recognition
Make fatigue part of your safety discussions and toolbox talks. -
Encourage sleep health
Promote sleep hygiene and offer wellness support for shift workers. -
Create a culture of safety
Encourage workers to speak up if they’re unfit for duty—without fear.
FAQ
How does Readi reduce accident risk?
By predicting fatigue before it impacts performance. Supervisors see risk windows in advance and can take action.
Does Readi require tracking or cameras?
No. Readi is non-invasive and can work with your ELD and scheduling data to predict fatigue in individuals. No GPS, video, or biometric data required.
Is Readi union-compliant?
Yes. Readi’s privacy-first model has been approved in sensitive, unionized operations.
How does it compare to fatigue alarms?
Fatigue alarms react after impairment. Readi predicts and prevents it—reducing false alarms by 58% when used together.
Related Posts
-
Can You Predict Fatigue Risk in Mining Without Wearables? New Research on Survey-Based Deep Learning Techniques for Measuring Fatigue Says YesFatigue is one of the biggest safety and performance risks in mining operations and other heavy industries. Workers who are tired...
-
An Interview with International Mining Magazine: A New Approach to Fatigue Management in MiningMining safety has always relied on layers of protection. What’s changing now is where those layers start.
-
Shifting From Reactive Dash Cam Safety to a Proactive Safety StrategyDash cams are now common across trucking fleets, mine sites, and people-transport operations. They help reconstruct incidents,...