In Canada, mining operations are subject to stringent regulations governing shift lengths to ensure the safety and well-being of workers. These legal requirements, which vary by province, are influenced by both federal and provincial legislation, making it crucial for HR professionals and compliance officers in the mining industry to stay informed.
Download the fatigue management policy template.
Understanding the specific regulations and standards for work hours and shift lengths is essential for maintaining compliance with labor laws and managing workforce scheduling effectively. Failing to adhere to these requirements can lead to penalties, legal liabilities, and concerns related to employee well-being and safety.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the definition of shift length requirements for mining operations in Canada, exploring the maximum hours per day and week, as well as the required rest periods between shifts. By the end of this article, HR professionals and business owners in the mining sector will have a clear understanding of their obligations and how to ensure compliance with provincial and federal regulations.
Definition of Shift Length Requirements for Mining Operations
Shift length requirements for mining operations in Canada are defined by a combination of federal and provincial regulations, which set out the maximum hours per day and week, as well as the required rest periods between shifts. These requirements are designed to protect the health and safety of workers in the mining industry, where long hours and demanding work conditions can lead to fatigue and increased risk of accidents.
Maximum Hours per Day and Week
The Canada Labour Code, which applies to federally regulated industries, outlines basic work hours and conditions. While mining operations may not always fall under federal jurisdiction, the Code provides a foundation for understanding standard working hours and overtime requirements. Provincial mining labor laws Canada further define the maximum hours per day and week for mining operations within their jurisdiction.
For example, in British Columbia, the Mines Act and accompanying regulations set out the legal requirements for mining operations, including provisions for shift work and workers' health and safety. These regulations may specify the maximum number of hours a miner can work in a day or week, taking into account the unique demands and risks associated with the mining industry.
Required Rest Periods Between Shifts
In addition to maximum hours per day and week, shift length requirements for mining operations also include mandatory rest periods between shifts. These rest periods are crucial for ensuring that workers have sufficient time to recover from the physical and mental demands of their jobs, reducing the risk of fatigue-related accidents and injuries.
Provincial regulations, such as those in Ontario and British Columbia, typically stipulate the minimum number of hours that must elapse between the end of one shift and the beginning of the next. These rest periods may vary depending on the length of the shift and the specific mining operation.
- Importance of Rest Periods: Adequate rest periods between shifts are essential for maintaining the health and well-being of mining workers. Fatigue can impair judgment, reaction time, and decision-making abilities, increasing the likelihood of accidents and injuries in an already high-risk work environment.
- Compliance with Rest Period Requirements: Employers in the mining industry must ensure that they are scheduling shifts in a manner that allows for the required rest periods between shifts. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in penalties and legal liabilities, as well as putting the safety of workers at risk.
Legal Framework for Shift Lengths in Canadian Mining
The regulatory landscape for shift lengths in Canadian mining is shaped by a combination of federal and provincial guidelines. These frameworks ensure that the health and safety of mining employees remain a priority across different operational contexts within Canada.
Federal Guidelines and Labour Standards
For mining operations under federal oversight, the Canada Labour Code establishes foundational standards regarding work hours and conditions. This code is instrumental in setting the parameters for what constitutes fair work practices and employee entitlements within the mining industry, ensuring:
- Baseline Work Hours: It sets a standard framework for acceptable daily and weekly work hours, ensuring that any extensions are justified through appropriate channels.
- Compensation for Extended Hours: The code clarifies the circumstances under which additional compensation for extended hours is required, safeguarding workers from potential exploitation.
Provincial Safety and Operational Protocols
Provincial regulations are tailored to address the distinct challenges and risks inherent in their specific mining environments. These protocols are meticulously crafted to enhance safety and operational efficiency, reflecting local workforce needs. Examples include:
- British Columbia: The Mines Act governs mining operations, providing specific guidelines to ensure safe shift practices and adequate rest periods for miners.
- Ontario: Regulations under the Occupational Health and Safety Act (OHSA) focus on minimizing occupational hazards and fostering a safe working environment through strict compliance measures.
Flexibility and Exemptions in Work Hours for Mining
The mining industry benefits from certain exemptions that allow flexibility in managing shift lengths, accommodating the sector's unique operational demands while maintaining safety standards:
- Work Hour Averaging: Agreements permit calculation of work hours over specified periods, facilitating longer shifts without breaching standard overtime rules.
- Special Conditions: Provisions exist for deviations from typical work hours based on operational needs or geographical considerations, provided these do not compromise worker safety.
By navigating these legal frameworks, HR leaders and compliance officers can ensure their mining operations adhere to legal standards while maintaining a robust focus on safety and productivity.
Factors Influencing Shift Length Policies
In the mining sector, shift length policies are shaped by a multitude of factors that address both operational demands and worker welfare. These considerations ensure the industry maintains productivity while prioritizing the health and safety of its workforce. The balance of these factors is critical in crafting policies that align with the strategic objectives of mining operations.
Worker Fatigue and Safety Protocols
The physical demands of mining necessitate a focus on managing worker fatigue to uphold safety standards. Excessive work hours can compromise alertness, leading to potential safety issues. Mining companies, therefore, adopt strategies that:
- Implement Safety Measures: Introduce structured rest intervals within shifts to maintain high levels of vigilance and prevent fatigue-related incidents.
- Conduct Regular Assessments: Evaluate shift schedules frequently to adapt to changing safety needs, ensuring a proactive approach to worker welfare.
Operational Challenges and Remote Site Management
Many mining sites operate in isolated areas, presenting unique challenges that influence shift scheduling. These remote locations often require adaptations to maximize operational efficiency. Companies address these challenges by:
- Enhancing On-Site Productivity: Structuring shifts to minimize downtime and make the most of the time spent on-site, which is critical for remote operations.
- Facilitating Workforce Logistics: Designing shift patterns that accommodate the logistical complexities of transporting workers to and from remote locations, ensuring a seamless operation.
Balancing Productivity and Workforce Agreements
Achieving productivity targets is a primary goal for mining operations, but this must be balanced with fair labor practices upheld by workforce agreements. This balance is achieved through:
- Adhering to Labor Agreements: Ensuring that shift structures are compliant with union agreements, which protect worker rights while enabling operational efficiency.
- Strategic Shift Design: Creating shift schedules that optimize productivity without overextending workers, supporting both company goals and employee well-being.
By considering these factors, mining operations develop shift length policies that not only meet legal and operational requirements but also foster a safe and productive working environment.
Standard Shift Schedules in the Mining Industry
The mining industry relies on carefully structured shift schedules to navigate the sector's unique demands, ensuring both productivity and the welfare of employees. These schedules are crafted to handle the industry's challenges, optimizing operational capacity while adhering to regulatory guidelines.
12-Hour Shifts
In Canadian mining, the 12-hour shift model is widely implemented to foster continuous operation with minimal disruptions. This approach reduces the frequency of shift transitions, thereby optimizing the use of machinery and personnel.
- Streamlined Operations: Longer shifts facilitate uninterrupted processes, reducing the need for frequent handovers. This continuity is crucial in maintaining efficient workflows, allowing for comprehensive task completion within a single shift cycle.
- Worker Resilience: The extended hours necessitate robust support systems to maintain worker performance. Companies often provide amenities and structured downtime to sustain energy levels, ensuring tasks are completed efficiently without compromising worker well-being.
Rotating Day and Night Shifts
To maintain round-the-clock productivity, many mining operations implement rotating day and night shifts. This system balances the workload among employees, supporting consistent production while mitigating the impact of non-standard work hours.
- Fair Distribution: By rotating shifts, companies evenly distribute the challenges of night work across their teams, preventing overburdening specific groups and promoting fairness.
- Flexibility in Operations: This scheduling model enables adaptability to changing operational demands and external factors, adjusting workforce deployment to meet strategic goals and market conditions.
Extended Workweeks
For mines in isolated locations, extended workweeks, such as a two weeks on, two weeks off schedule, are common. This model addresses the logistical complexities of remote work environments, ensuring workers have substantial rest periods to recuperate.
- Efficient Resource Management: Extended workweeks reduce the logistical burden of frequent commutes, optimizing time and resources by minimizing travel to and from remote sites.
- Sustaining Workforce Engagement: By offering lengthy rest periods between rotations, this schedule supports a sustainable work-life balance, enhancing job satisfaction and retention rates among employees.
These shift schedules are integral to mining operations, balancing the necessity of continuous production with the imperative of maintaining a healthy and efficient workforce. By tailoring shifts to the industry's unique challenges, companies can achieve their operational objectives while safeguarding employee welfare.
Modifications and Exemptions to Standard Hours of Work
The mining industry necessitates adjustments to standard work hours to ensure efficiency and safety. These modifications, while providing necessary flexibility, remain bound by regulations to uphold worker health and productivity. Companies focus on aligning operational requirements with compliance, ensuring that any schedule deviations serve both business and employee interests.
Flexible Scheduling and Workload Management
Flexible scheduling is crucial for managing workload variations in mining. This approach allows the distribution of work hours over a designated period, accommodating operational peaks without exceeding standard limits. This flexibility is particularly beneficial in mining, where:
- Dynamic Resource Allocation: Companies can reallocate workforce hours efficiently to match operational demands, minimizing unnecessary overtime and optimizing productivity.
- Employee Empowerment: By providing predictable work patterns, employees can better manage their personal and professional obligations, enhancing overall job satisfaction.
Prolonged Work Periods with Strategic Rest
In certain situations, mining operations may implement prolonged work periods balanced with strategic rest days to meet operational goals while ensuring worker recovery. This model supports sustained productivity through:
- Comprehensive Project Execution: Extended work periods allow for the seamless progression of mining tasks, reducing disruptions caused by frequent shift changes.
- Enhanced Recovery Opportunities: By strategically scheduling rest days, companies ensure that employees have ample time to recuperate, which is essential for maintaining high levels of performance in demanding roles.
Customized Safety Protocols
Health and safety codes in mining often include tailored protocols that align with the sector's unique challenges while prioritizing worker safety. These customized guidelines address the specific risks inherent in mining operations, ensuring:
- Site-Specific Safety Measures: Protocols are adapted to the distinct conditions of each mining site, providing comprehensive protection against potential hazards.
- Regulatory Assurance: By adhering to these specialized safety standards, mining companies maintain compliance with legal requirements, thereby reducing liability risks and enhancing their operational integrity.
Through these strategic modifications and exemptions, mining operations can effectively navigate their complex environments, achieving operational objectives while maintaining a strong commitment to employee well-being and safety.
Ensuring Compliance with Shift Length Requirements
In the mining industry, adhering to shift length regulations is critical not only for legal compliance but also for safeguarding worker health. Implementing a comprehensive framework that includes effective record management, proactive fatigue strategies, and thorough oversight is essential for maintaining a safe and compliant work environment.
Accurate Record-Keeping of Hours Worked
Effective compliance starts with diligent tracking and documentation of employee work hours. This practice not only supports legal adherence but also enhances operational transparency. Mining operations often employ sophisticated time-tracking solutions to maintain precision:
- Automated Time-Tracking Systems: These systems ensure that work hours are logged accurately, reducing errors and providing real-time insights into workforce patterns. This data helps identify areas for operational improvements and compliance verification.
- Routine Audits: By conducting regular audits of time records, companies can ensure consistency with legal standards. These reviews help detect any discrepancies early, allowing for timely corrective actions.
Fatigue Management Plans and Training
Addressing worker fatigue proactively is critical for both safety and productivity. Implementing comprehensive fatigue management plans involves educating the workforce and equipping them with tools to manage fatigue effectively:
- Comprehensive Training Initiatives: Regular training sessions empower employees to understand and mitigate fatigue risks. These initiatives highlight the importance of effective rest and recuperation, embedding a safety-first mindset within the workforce.
- Tailored Fatigue Solutions: Customizing fatigue management to align with specific job roles and individual needs enhances its effectiveness. By recognizing diverse operational demands, companies can implement solutions that maintain high performance levels and minimize safety risks.
Regular Monitoring and Audits by Regulators
Ensuring compliance with shift length requirements relies heavily on consistent regulatory oversight. Regular inspections and audits by relevant authorities play a vital role in maintaining industry standards and worker protections:
- Scheduled Compliance Reviews: Routine assessments by regulatory bodies confirm that mining operations adhere to established shift length guidelines. These reviews provide an additional layer of accountability, ensuring robust compliance practices are in place.
- Engagement with Regulatory Authorities: By fostering collaborative relationships with regulators, mining companies can address compliance challenges proactively. Open communication channels keep operations informed of regulatory updates, enhancing their ability to adapt and comply with evolving standards.
By integrating precise record-keeping, strategic fatigue management, and rigorous regulatory oversight, mining operations can ensure compliance with shift length regulations. This approach not only upholds legal standards but also reinforces a culture of safety and operational excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Navigating the regulatory environment of Canadian mining operations involves understanding specific nuances related to shift scheduling. This section aims to clarify common inquiries that HR professionals and compliance officers face, ensuring a clear grasp of the legal landscape.
What are the maximum shift lengths allowed for mining operations in Canada?
Shift lengths in Canadian mining are regulated primarily at the provincial level, tailored to address the demands and safety concerns inherent in the industry. These regulations focus on balancing operational efficiency with employee well-being. Key points include:
- Provincial Guidelines: Most provinces stipulate a cap on daily shifts, often around 12 hours, to manage fatigue and ensure safety. This helps maintain a consistent approach to worker health across the sector.
- Flexibility for Operational Needs: In certain situations, exceptions to standard shift lengths can be granted, provided that stringent safety protocols are in place. Such flexibility is crucial for adapting to the dynamic operational requirements of mining activities.
How do provincial regulations differ regarding shift lengths in mining?
Provincial variations in mining regulations reflect the diverse operational contexts and geographical challenges across Canada. These differences underscore the necessity for companies to adapt their compliance strategies to local conditions:
- Diverse Regulatory Frameworks: Each province implements specific mandates that cater to regional mining characteristics, such as remote site operations or environmental considerations. For example, certain provinces may emphasize more robust safety measures due to unique geographic conditions.
- Adaptation to Local Needs: Some provinces offer regulatory leeway to accommodate the sector's evolving demands, allowing companies to modify shift patterns while maintaining safety and compliance. This adaptability ensures that operational objectives can be met without compromising worker welfare.
These frequently asked questions are designed to provide clarity on how mining operations can align their practices with legal requirements, fostering a compliant and secure work environment.
Related Posts
-
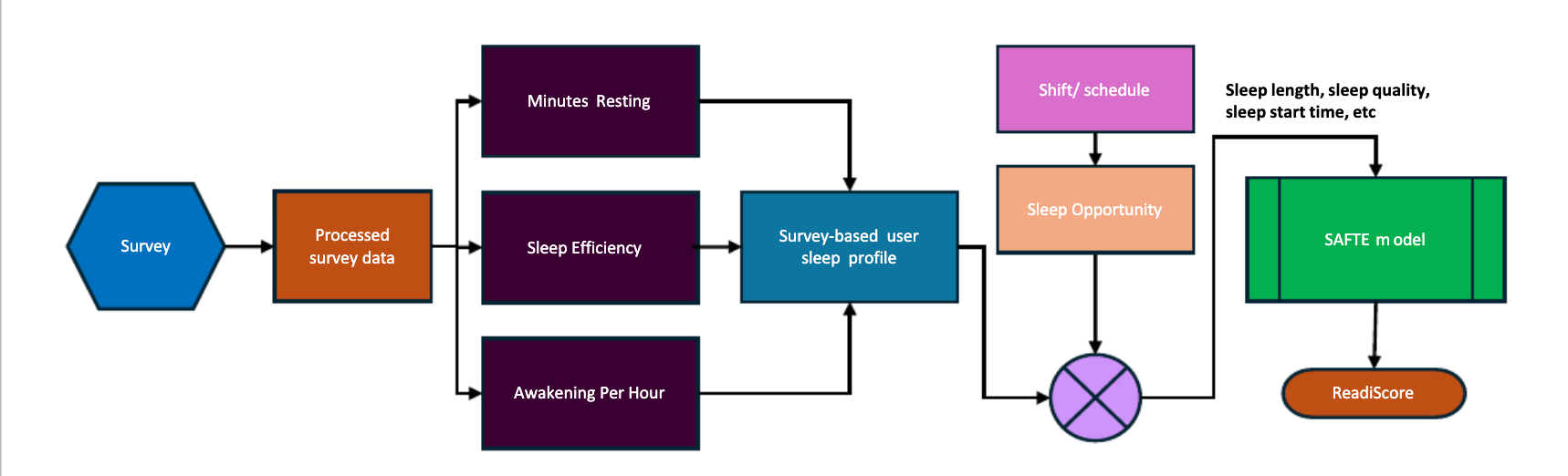
Can You Predict Fatigue Risk in Mining Without Wearables? New Research on Survey-Based Deep Learning Techniques for Measuring Fatigue Says YesFatigue is one of the biggest safety and performance risks in mining operations and other heavy industries. Workers who are tired...
-
An Interview with International Mining Magazine: A New Approach to Fatigue Management in MiningMining safety has always relied on layers of protection. What’s changing now is where those layers start.
-
The Future of Occupational Health in the AI EraThe workplace safety landscape is undergoing a fundamental transformation as artificial intelligence reshapes how organizations...