What You Need to Know About Shift Length Laws in US Mining
Mining operations in the United States play a vital role in the nation's economy, providing essential resources for various industries. However, ensuring the safety and well-being of miners is of utmost importance.
The Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) is the primary regulatory body responsible for overseeing mining operations and enforcing compliance with mandatory safety and health standards. One critical aspect of these regulations is the management of shift lengths to prevent fatigue and maintain a safe working environment.
While there are no specific federal laws dictating exact shift lengths for mining operations, MSHA emphasizes the importance of managing worker fatigue as a crucial component of mine safety. Prolonged shifts can lead to fatigue, increasing the risk of accidents and compromising the health and well-being of miners.
Maximum Shift Lengths Allowed by MSHA
MSHA sets limits on the maximum number of hours miners can work per shift to ensure their safety and prevent excessive fatigue. For underground mining operations, shifts are generally limited to 8 hours, with some exceptions based on the specific nature of the work and the conditions of the mine.
Surface mining operations, on the other hand, have more flexibility in terms of shift lengths. However, they must still adhere to MSHA guidelines and implement appropriate measures to manage fatigue and ensure the safety of their workers.
It's important to note that while MSHA provides general guidelines on shift lengths, some states may have additional regulations or requirements that mining operations must comply with. These state-specific regulations can vary and may impose stricter limits on work hours or require additional rest periods between shifts.
Regulations Governing Work Hours in Mining
The regulatory framework for work hours in mining is primarily anchored by the Federal Mine Safety and Health Act of 1977. This pivotal piece of legislation establishes comprehensive mandates to minimize hazardous exposures in mining activities. Through its enforcement, MSHA ensures that mining operations comply with essential safety standards, which prioritize the protection of workers.
Delving further into the specifics, MSHA's detailed regulations are encapsulated in 30 CFR Parts 1-199. These regulations outline a broad spectrum of operational parameters, including the necessity for scheduled breaks, which play a key role in sustaining miner vigilance and mitigating risks associated with exhaustion. By defining maximum daily and weekly hours, these standards seek to avert the adverse effects of excessive work and guarantee sufficient rest for miners.
The regulations also provide for specific exemptions, recognizing that mining operations can differ significantly in their operational requirements. Certain circumstances may allow for deviations from standard shift lengths, but these exceptions are stringently controlled to maintain miner safety as the central focus. This regulatory approach highlights the balance between operational adaptability and strict adherence to safety guidelines, ensuring that the health of miners remains a priority.
How MSHA Enforces Shift Length Compliance
The Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) employs a comprehensive enforcement strategy to ensure that mining operations comply with shift length regulations. Their process involves detailed inspections that focus on upholding safety standards and preventing potential violations. MSHA inspectors are integral to this effort, conducting thorough evaluations to verify adherence to established guidelines.
During inspections, MSHA inspectors review various operational documents and engage with miners to gather insights. This approach allows them to cross-check the accuracy of reported work hours and ensure that shift schedules reflect actual practices. By speaking directly with miners, inspectors gain critical perspectives on the working conditions, ensuring alignment between documentation and reality.
Mining operators must maintain detailed time and payroll records for each miner to demonstrate compliance. These records provide essential data for MSHA inspections, offering a comprehensive view of shift lengths and scheduling practices. Maintaining accurate documentation not only aids in compliance verification but also highlights the operator's dedication to safety standards. This transparency ensures any discrepancies are promptly addressed, reinforcing the safety of the mining workforce.
Furthermore, operators may be required to display shift schedules prominently to demonstrate adherence to MSHA's guidelines. This practice enhances visibility and allows inspectors and miners to easily verify compliance with shift length regulations. By ensuring clear and accessible records, mining operations support a culture of accountability and contribute to a safer, more compliant work environment.
Consequences of Violating Shift Length Regulations
Non-compliance with MSHA's shift length regulations can lead to significant consequences, affecting both operational efficiency and legal standing. MSHA enforces these standards rigorously, and any infringement can result in immediate corrective actions mandated by citations and orders. These interventions are essential to maintaining safety and compliance within the industry.
Fines for not adhering to shift length standards are substantial, emphasizing the critical nature of safety compliance. An initial violation can result in penalties of up to $250,000, reflecting the serious nature of these regulations. Subsequent violations can incur even steeper fines, potentially reaching $500,000 for repeat offenses. These financial repercussions are designed to dissuade non-compliance and reinforce the importance of safeguarding miner welfare.
In addition to financial penalties, operators may face legal repercussions if violations are found to be intentional. Such legal actions highlight the ethical and regulatory responsibilities of mining companies to protect their workforce. Criminal charges not only jeopardize a company's reputation but also pose significant operational challenges, underscoring the necessity for adherence to MSHA's shift length regulations. Maintaining compliance is essential to fostering a safe and legally sound mining operation.
Requirements for Breaks During Mining Shifts
Providing miners with regular breaks during their shifts is a crucial component of a safe and effective mining operation. MSHA regulations mandate that mining operations incorporate sufficient rest periods into their scheduling to mitigate fatigue and lower the risk of workplace accidents. These breaks are vital for maintaining not only the physical health of miners but also their mental acuity in a demanding work environment.
The specifics of break requirements vary across different mining sectors and operational types. For instance, underground mining operations may require more frequent breaks due to the physically demanding nature and environmental conditions faced by miners. Conversely, surface mining operations, while generally offering more operational flexibility, must still adhere to well-defined break schedules to ensure all workers receive necessary rest throughout their shifts.
Access to clean drinking water is another essential requirement under MSHA standards, emphasizing the importance of hydration in maintaining miner safety and performance. This is particularly critical in environments where physical exertion is high and temperatures can be extreme. Ensuring miners have continual access to potable water not only supports their health but also enhances their ability to perform their duties effectively, aligning with regulatory expectations for a safe and sustainable working environment.
Exemption for Overtime Pay in Mining
The mining industry functions under specific labor regulations that accommodate its unique operational characteristics, such as those outlined in the Federal Mine Safety and Health Act of 1977. Within this framework, the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) provides a partial exemption from overtime pay for miners, acknowledging the sector’s distinct demands and operational conditions.
Nevertheless, miners are required to receive overtime pay for hours worked beyond the standard 40-hour workweek, ensuring that extended shifts are fairly compensated. This provision underlines the commitment to maintaining equitable compensation practices, recognizing the critical balance between operational needs and employee welfare.
Furthermore, individual states may have their own overtime pay regulations that mining operators must consider in addition to federal standards. These state-specific rules can introduce additional requirements, underscoring the importance of understanding and adhering to both federal and local labor laws. By doing so, mining operations uphold ethical labor practices and foster a compliant industry environment.
Shift Scheduling Best Practices in Mining
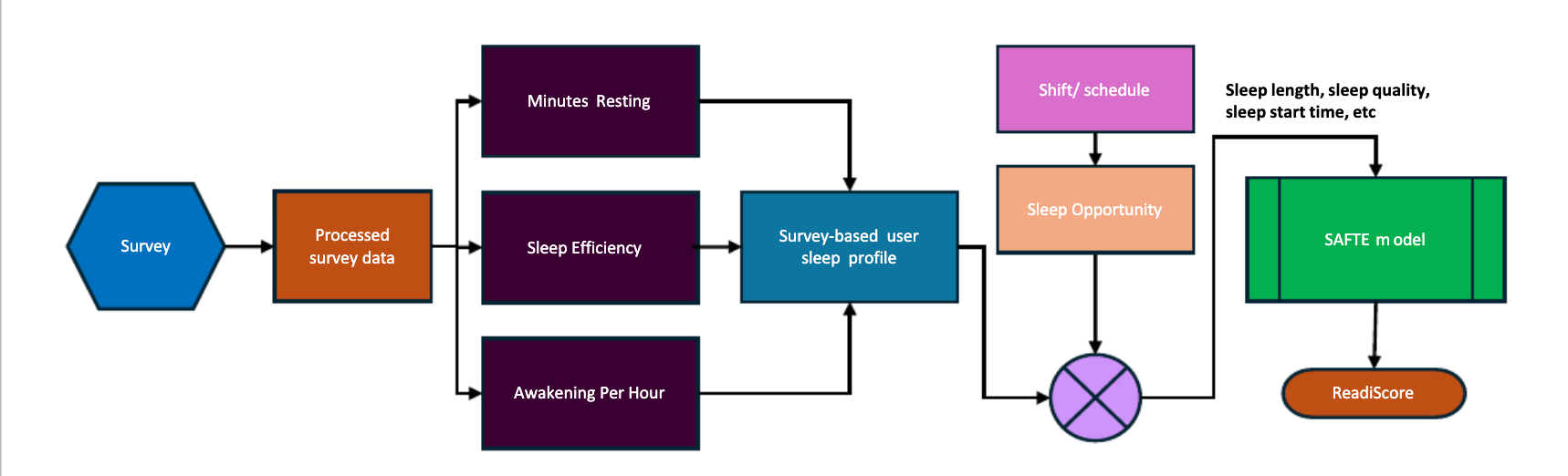
Successfully managing shift schedules in mining operations demands a strategic approach that balances productivity with worker safety. Incorporating innovative tools like fatigue risk management systems becomes crucial in this endeavor. Technologies such as fatigue modeling software offer predictive analytics, assessing variables such as shift patterns, environmental conditions, and individual health data. By leveraging these insights, mining operators can foresee potential fatigue issues and adjust schedules proactively to enhance workforce well-being.
A robust fatigue management plan underpins successful shift scheduling strategies, ensuring continuous monitoring and proactive mitigation of fatigue risks. Such plans should include clear guidelines for identifying and addressing fatigue, providing educational resources to workers about rest and recovery, and maintaining open channels for reporting fatigue-related concerns. Regular evaluation and updates to these plans ensure they remain relevant and effective, adapting to any operational changes or emerging challenges. This commitment to fatigue management not only bolsters safety but also supports sustained productivity.
Consistent review and optimization of time records and scheduling practices are integral to maintaining regulatory compliance and minimizing overtime. This process involves a detailed examination of work patterns to identify any scheduling inefficiencies or potential risks. Accurate record-keeping supports alignment with legal standards and enhances transparency within the organization. By fostering a culture of accountability and continuous improvement, mining operators can ensure a safe and efficient work environment that prioritizes the health and safety of their workforce.
Related Posts
-
Can You Predict Fatigue Risk in Mining Without Wearables? New Research on Survey-Based Deep Learning Techniques for Measuring Fatigue Says YesFatigue is one of the biggest safety and performance risks in mining operations and other heavy industries. Workers who are tired...
-
An Interview with International Mining Magazine: A New Approach to Fatigue Management in MiningMining safety has always relied on layers of protection. What’s changing now is where those layers start.
-
The Future of Occupational Health in the AI EraThe workplace safety landscape is undergoing a fundamental transformation as artificial intelligence reshapes how organizations...