How to Monitor and Manage Fatigue in Mining Workers
Mining operations run 24/7, with workers often logging long hours in challenging environments. While the industry has made significant strides in improving safety, one persistent risk remains: worker fatigue.
DOWNLOAD THE BUYER'S GUIDE OT READI TO LEARN EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW TO PURCHASE AND IMPLEMENT OUR PREDICTIVE FATIGUE RISK MANAGEMENT SYSTEM.
Fatigue in mining is more than just feeling tired; it's a state of mental and physical exhaustion that can impair judgment, slow reaction times, and increase the likelihood of accidents. The consequences can be severe, ranging from decreased productivity to life-threatening incidents.
Recognizing the gravity of this issue, mining companies are increasingly turning to fatigue management strategies to mitigate risks and protect their workforce. By implementing comprehensive fatigue management programs, they aim to create a safer, healthier, and more productive work environment.
What is fatigue management in mining?
Fatigue management in mining is a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and controlling fatigue-related risks. It involves a combination of strategies, policies, and technologies designed to minimize the impact of fatigue on worker safety and operational efficiency.
The goal of fatigue management is to ensure that workers are alert, focused, and capable of performing their duties safely throughout their shifts. This is achieved through a multi-faceted approach that addresses the root causes of fatigue, such as:
-
Shift scheduling: Designing work schedules that align with the body's natural circadian rhythms and allow for sufficient rest and recovery between shifts.
-
Workload management: Ensuring that workers have manageable workloads and adequate breaks to prevent excessive fatigue.
-
Sleep hygiene: Promoting healthy sleep habits and providing education on the importance of quality sleep for overall well-being and job performance.
-
Work environment: Optimizing the work environment to minimize fatigue-inducing factors, such as poor lighting, extreme temperatures, and excessive noise.
By implementing a comprehensive fatigue management program, mining companies can proactively address fatigue-related risks, enhance worker safety, and improve overall operational performance. This approach not only benefits the individual workers but also contributes to the long-term success and sustainability of the mining operation.
How to Monitor and Manage Fatigue in Mining Workers
Effectively monitoring and managing fatigue in mining workers requires a proactive, data-driven approach. This involves leveraging advanced technologies and best practices to identify fatigue risks, implement preventive measures, and continuously assess the effectiveness of the fatigue management program.
1. Implement a Predictive Fatigue Management System
Traditional fatigue management relies on reactive measures, such as monitoring for signs of fatigue during shifts. However, a more effective approach is to use predictive fatigue management tools that assess fatigue risks before shifts even begin.
Predictive fatigue management systems, such as those offered by Fatigue Science, use advanced algorithms and data analytics to forecast fatigue risk based on factors like sleep patterns, work schedules, and individual circadian rhythms. By identifying potential fatigue risks in advance, supervisors can take proactive measures to mitigate those risks, such as adjusting shift schedules or assigning less demanding tasks to at-risk workers.
2. Optimize Shift Scheduling
One of the most critical aspects of fatigue management in mining is shift scheduling. Poor shift design can significantly contribute to worker fatigue, increasing the risk of accidents and decreasing productivity.
To optimize shift scheduling for fatigue management, consider the following best practices:
-
Align shifts with natural circadian rhythms: Schedule shifts in a way that minimizes disruption to the body's natural sleep-wake cycle.
-
Limit consecutive night shifts: Consecutive night shifts can lead to chronic sleep deprivation and increased fatigue risk. Limit the number of consecutive night shifts and provide adequate recovery time between shifts.
-
Implement fatigue-reducing shift patterns: Some shift patterns, such as the forward-rotating schedule (day-afternoon-night), have been shown to reduce fatigue compared to backward-rotating schedules.
-
Use fatigue modeling tools: Fatigue modeling software, like Fatigue Science's Instant Insights, can help optimize shift schedules by predicting fatigue risk based on various shift patterns and identifying the most effective schedule for reducing fatigue.
3. Use Real-Time Fatigue Monitoring Technology
While predictive fatigue management is crucial for preventing fatigue-related incidents, real-time monitoring is still necessary to detect and respond to signs of fatigue during shifts. Real-time fatigue monitoring technology can provide instant alerts to supervisors when a worker shows signs of fatigue, allowing for immediate intervention.
Some examples of real-time fatigue monitoring technology include:
-
Camera-based systems: These systems use cameras to monitor workers' facial expressions and eye movements for signs of fatigue, such as drooping eyelids or head nodding.
-
Wearable devices: Wearable devices, like smartwatches or fitness trackers, can monitor workers' sleep patterns, heart rate, and activity levels to detect signs of fatigue.
-
Machine learning algorithms: Advanced machine learning algorithms can analyze data from various sources (e.g., cameras, wearables, and equipment sensors) to detect patterns indicative of fatigue.
It's important to note that while camera-based systems are widely used, they have limitations, particularly in underground mining environments where visibility may be poor. In these cases, wearable devices or machine learning algorithms that don't rely on visual data may be more effective.
4. Educate Workers and Supervisors on Fatigue Management
Effective fatigue management in mining requires a team effort. Both workers and supervisors must be educated on the signs, symptoms, and risks of fatigue, as well as strategies for managing it.
Some key topics to cover in fatigue management training include:
-
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of fatigue: Workers should be trained to recognize the physical, mental, and emotional signs of fatigue in themselves and their coworkers.
-
Fatigue countermeasures: Workers should be taught effective strategies for managing fatigue, such as taking breaks, staying hydrated, and practicing good sleep hygiene.
-
Reporting fatigue concerns: Encourage workers to report fatigue concerns to their supervisors without fear of reprisal. Foster an open, supportive culture where fatigue is recognized as a safety issue, not a personal failing.
-
Supervisor responsibilities: Train supervisors on how to recognize signs of fatigue in their team members, how to respond appropriately, and when to intervene to ensure safety.
Regular training and open communication about fatigue can help create a culture of safety and awareness, where everyone is committed to managing fatigue and promoting worker well-being.
5. Regularly Review and Update Fatigue Management Strategies
Fatigue management in mining is an ongoing process. As new technologies emerge and best practices evolve, it's essential to regularly review and update your fatigue management strategies to ensure they remain effective.
Some key steps in this process include:
-
Monitoring fatigue-related incidents: Regularly review incident reports and investigate any fatigue-related incidents to identify areas for improvement.
-
Analyzing fatigue data: Use data from fatigue monitoring systems and worker feedback to identify patterns and trends in fatigue risk.
-
Updating policies and procedures: Based on your analysis, update your fatigue management policies and procedures to address any identified gaps or weaknesses.
-
Continuous improvement: View fatigue management as a continuous improvement process. Regularly assess the effectiveness of your strategies and make adjustments as needed to optimize worker safety and well-being.
By regularly reviewing and updating your fatigue management strategies, you can ensure that your program remains responsive to the changing needs of your workforce and the evolving challenges of the mining industry.
Tips on Best Practices for Fatigue Management in Mining
Implementing an effective fatigue management program in mining requires a strategic, data-driven approach. Here are some best practices to consider:
1. Assess Gaps and Risks
Before implementing a fatigue management program, conduct a thorough assessment of your current practices and potential fatigue-related risks. This may involve:
-
Reviewing incident reports and safety data to identify any fatigue-related trends
-
Conducting worker surveys and focus groups to gather feedback on fatigue concerns
-
Analyzing shift schedules and workload patterns to identify potential fatigue hotspots
By assessing your current state through a fatigue risk assessment, you can identify gaps in your fatigue management practices and prioritize areas for improvement.
2. Incorporate Technology
Leveraging advanced predictive fatigue risk management technology can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your fatigue management program. Some key technologies to consider include:
-
Predictive fatigue modeling software, like Fatigue Science's Readi, to optimize shift schedules and proactively identify fatigue risks
-
Real-time fatigue monitoring systems, such as wearable devices like the ReadiWatch or machine learning algorithms, to detect signs of fatigue during shifts
-
Fatigue risk management platforms that integrate data from multiple sources (e.g., scheduling, incident reports, and monitoring systems) to provide a comprehensive view of fatigue risk across your operation
By incorporating technology into your fatigue management program, you can gain valuable insights into fatigue patterns, make data-driven decisions, and implement targeted strategies to mitigate risks.
3. Foster a Safety-First Culture
Ultimately, the success of your fatigue management program depends on the commitment and engagement of your workforce. To foster a safety-first culture that prioritizes fatigue management:
-
Communicate the importance of fatigue management regularly and consistently
-
Involve workers in the development and implementation of fatigue management strategies
-
Encourage open reporting of fatigue concerns and incidents without fear of reprisal
-
Recognize and reward workers and teams who demonstrate a commitment to fatigue management and safety
By creating a culture where fatigue is recognized as a critical safety issue and everyone is empowered to take responsibility for managing it, you can build a more resilient, safe, and productive mining operation.
FAQs
Q: What are the signs and symptoms of fatigue in mining workers?
A: Some common signs and symptoms of fatigue in mining workers include:
-
Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
-
Slowed reaction times
-
Increased errors or accidents
-
Irritability or mood changes
-
Physical symptoms such as yawning, heavy eyelids, or microsleeps
Q: How does fatigue impact safety and productivity in mining operations?
A: Fatigue can have a significant impact on safety and productivity in mining operations. Fatigued workers are more likely to make errors, have slower reaction times, and be involved in accidents. This can lead to increased safety incidents, equipment damage, and lost productivity. In extreme cases, fatigue-related incidents can result in serious injuries or fatalities.
Q: What are the legal requirements for fatigue management in the mining industry?
A: Legal requirements for fatigue management in the mining industry vary by jurisdiction. However, in general, mining companies are required to provide a safe working environment and take steps to mitigate fatigue-related risks. This may include implementing fatigue management plans, conducting fatigue risk assessments, and providing worker training on fatigue management. It's essential to consult with legal and regulatory experts to ensure compliance with all applicable requirements.
Q: How can technology help in managing fatigue among mine workers?
A: Technology can play a crucial role in managing fatigue among mine workers. Predictive fatigue modeling software can help optimize shift schedules to minimize fatigue risk. Real-time fatigue monitoring systems, such as wearables or camera-based systems, can detect signs of fatigue during shifts and alert supervisors to intervene. Fatigue risk management platforms can integrate data from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive view of fatigue risk across the operation, enabling data-driven decision-making and targeted interventions.
Q: What are the best practices for fatigue management in mining?
A: Some best practices for fatigue management in mining include:
-
Conducting fatigue risk assessments to identify gaps and priorities
-
Designing fatigue-reducing shift schedules that align with circadian rhythms
-
Implementing predictive and real-time fatigue monitoring technologies
-
Providing regular fatigue management training for workers and supervisors
-
Fostering a safety-first culture that encourages open reporting and proactive management of fatigue
-
Regularly reviewing and updating fatigue management strategies based on data and worker feedback
By implementing these best practices, mining companies can create a comprehensive, data-driven approach to fatigue management that prioritizes worker safety, well-being, and operational efficiency.
How to Monitor and Manage Fatigue in Mining Workers
Mining workers often endure demanding conditions that contribute to fatigue—prolonged shifts, variable hours, and challenging environments can all impact their well-being. Effectively tackling fatigue involves a multifaceted strategy that not only identifies potential fatigue risks but also implements measures to prevent them. The objective: to maintain a secure and streamlined operational environment where fatigue-related incidents are minimized.
Identifying Fatigue Risks
Pinpointing the root causes of fatigue is essential to crafting an effective management plan. Environmental factors such as harsh weather conditions and high noise levels can intensify fatigue, as can the physical demands inherent in mining tasks. Regular evaluations of these conditions, supported by direct worker input, can reveal specific risks. This insight allows for precise interventions, tailored to the unique challenges of the mining sector.
Implementing Preventive Measures
Preventive measures form the core of a robust fatigue management strategy. Establishing guidelines that ensure regular breaks and adequate rest are critical. Additionally, cultivating an organizational culture that prioritizes sleep health can significantly enhance worker alertness. Initiatives might include training programs that highlight the importance of restful sleep and offer practical strategies for achieving it, such as maintaining a consistent sleep routine and optimizing sleep environments.
Leveraging Technology
Advanced technology provides essential tools for anticipating and managing fatigue. Systems that predict fatigue levels, often using complex data analysis, enable supervisors to act before issues escalate.
These tools incorporate variables such as shift patterns and accumulated sleep data to identify when a worker might face heightened fatigue risk, allowing for timely adjustments.
By transitioning from reactive to predictive management, these technologies can significantly reduce fatigue-related incidents.
Unlike reactive approaches, which often rely on post-factum alerts like camera-based systems, predictive solutions analyze potential risk factors well ahead of time, allowing for strategic interventions. This forward-thinking approach not only bolsters safety but also improves productivity by ensuring workers maintain optimal performance throughout their shifts. Integrating these strategies into a comprehensive fatigue management program can fundamentally enhance how mining operations address fatigue, fostering safer and more efficient work environments.
1. Implement a Predictive Fatigue Management System
Adopting a predictive fatigue management system can revolutionize how fatigue risks are managed. By leveraging cutting-edge technology, these systems can anticipate and address potential fatigue issues before they arise. This proactive approach not only enhances safety but also optimizes workflow efficiency. With these systems, you can strategically plan and allocate resources to minimize the risk of fatigue-related incidents.
Predictive systems utilize a comprehensive analysis of work patterns, environmental conditions, and worker data to pinpoint potential fatigue risks. By understanding how factors like shift length and work intensity interact with natural sleep cycles, managers can design rosters that enhance alertness and reduce fatigue. This data-driven strategy ensures that tasks are aligned with workers' peak performance times, minimizing errors and boosting overall productivity.
A prime example of this technology is a system that integrates seamlessly with existing operations, providing real-time insights based on sophisticated data modeling. These predictive tools process a wide range of data inputs to deliver accurate forecasts of fatigue risks. This empowers supervisors to make informed decisions, such as adjusting task assignments and optimizing shift rotations. By identifying potential fatigue challenges early, such systems help maintain a safe and efficient work environment, ensuring that issues are proactively managed before they affect safety and performance.
2. Optimize Shift Scheduling
Effective shift scheduling is essential in mitigating fatigue risks in mining operations. By designing work schedules that consider the natural ebb and flow of human alertness throughout the day, workers can maintain higher levels of energy and focus. This strategic alignment with biological rhythms minimizes the likelihood of fatigue-related incidents, enhancing both safety and productivity on site.
To find the most effective schedule, assess various shift patterns to identify which best supports worker health and operational efficiency. For example, implementing shifts that gradually transition start times can help reduce sleep debt accumulation. Consider the impact of shift length and frequency, ensuring adequate rest periods between shifts to promote recovery. This trial-and-error approach, informed by worker feedback and performance data, allows for the creation of a balanced schedule that meets both operational demands and the well-being of the workforce.
Technological tools provide invaluable insights for refining shift schedules. Utilizing predictive analytics and real-time data, these tools evaluate how different scheduling arrangements affect fatigue levels and overall performance. By integrating this information, managers can make informed decisions that prioritize worker safety and efficiency. Such technologies help create a responsive scheduling system that adapts to changing workforce needs and external conditions, fostering a proactive approach to fatigue management.
3. Use Real-Time Fatigue Monitoring Technology
Incorporating real-time monitoring systems in mining operations is essential for maintaining a proactive approach to worker safety. These systems continuously evaluate workers' alertness levels, providing a dynamic safety layer that adapts to the ever-changing conditions on site. By identifying fatigue risks as they develop, supervisors can take immediate actions, such as adjusting workloads or enforcing rest breaks, to mitigate potential hazards.
The deployment of these advanced systems involves using innovative technologies that capture and analyze various physiological signals indicative of fatigue. Technologies such as non-invasive sensors embedded in equipment and advanced analytics platforms offer insights into factors like cognitive responses and workload stress. These insights enable supervisors to make timely, data-driven decisions to enhance worker safety and performance.
When evaluating reactive versus proactive methodologies, the distinction lies in their strategic focus. Reactive systems typically alert supervisors after fatigue symptoms become apparent, necessitating quick responses to address immediate risks. Proactive solutions, however, leverage predictive analytics to anticipate fatigue risks based on patterns and trends. This approach not only prevents incidents but also enhances overall efficiency by ensuring workers remain at peak performance levels. Both methodologies are crucial, each contributing uniquely to a well-rounded fatigue management strategy.
4. Educate Workers and Supervisors on Fatigue Management
Education is a cornerstone of effective fatigue management strategies. Tailored training programs that delve into the complexities of fatigue can significantly enhance workers' ability to identify early warning signs in themselves and their peers. By focusing on the physiological and cognitive effects of fatigue, workers can be better prepared to recognize and mitigate risks before they impact safety or performance. This proactive education empowers workers to take control of their well-being and contributes to a more vigilant and responsive workforce.
Establishing a culture where fatigue-related discussions are normalized is crucial for maintaining operational safety. Encouraging workers to voice fatigue concerns cultivates an environment rooted in trust and mutual support. This open dialogue not only facilitates early detection of potential fatigue issues but also allows for collaborative problem-solving approaches. Regular forums or meetings dedicated to fatigue management can reinforce the importance of these discussions, ensuring that they remain a priority within the organizational culture.
Supervisors play a pivotal role in fatigue management and require targeted training to effectively address fatigue-related challenges. Providing supervisors with actionable strategies, such as dynamic task allocation and workload balancing, equips them to respond swiftly to fatigue indicators. Training should also focus on enhancing observational skills, enabling supervisors to spot subtle signs of fatigue and intervene appropriately. By preparing supervisors with these capabilities, organizations can ensure that fatigue management becomes an integral part of day-to-day operations, seamlessly enhancing both safety and efficiency.
5. Regularly Review and Update Fatigue Management Strategies
Incorporating a forward-thinking approach to managing fatigue involves routine evaluations of your current strategies. As the landscape of the mining industry shifts, so must the tactics used to combat worker fatigue. Continuous assessment allows for the integration of cutting-edge practices and technologies, ensuring that your workforce remains protected and efficient under evolving conditions.
Scheduled Assessments: Designate specific times for conducting thorough evaluations of fatigue protocols. This includes scrutinizing incident logs, gathering real-time feedback from employees, and analyzing operational data to pinpoint emerging challenges. Engaging directly with those on the front lines provides crucial insights into the daily impact of fatigue management efforts, ensuring they are both practical and effective.
Insight-Driven Adjustments: Utilize advanced analytic tools to decipher patterns and recognize areas needing enhancement. For instance, examining the correlation between fatigue levels and specific operational tasks can reveal underlying issues such as inadequate recovery periods or excessive demands. These insights enable the fine-tuning of work schedules and task distribution, ensuring that strategies are not only current but also aligned with the latest industry benchmarks.
Formulating a Comprehensive Strategy: Develop a detailed fatigue management strategy that clearly outlines objectives, assigns responsibilities, and specifies monitoring and intervention procedures. This strategy should be flexible enough to incorporate ongoing feedback and continuous learning, while also aligning with current health and safety standards. Regularly update all stakeholders, promoting an organizational culture that values proactive fatigue management and continuous advancement.
By integrating these elements into your fatigue management approach, you ensure that your strategies are not only reactive but also anticipatory, effectively minimizing fatigue-related risks while supporting the well-being and productivity of your workforce.
Tips on Best Practices for Fatigue Management in Mining
1. Evaluate Current Practices and Identify Weaknesses
To effectively manage fatigue in mining, begin by evaluating your existing processes and identifying potential weaknesses. This involves a comprehensive review of operational demands, environmental stressors, and worker feedback. Through this evaluation, you'll gain insights into the specific conditions that contribute to fatigue, allowing you to tailor interventions accordingly. Regular updates to these evaluations ensure that emerging risks are swiftly addressed.
Gathering input directly from the workforce can reveal day-to-day challenges that may not be immediately apparent. Combine this feedback with quantitative data, such as performance metrics and safety records, to establish a holistic understanding of fatigue in your operation. This approach helps prioritize areas for improvement and ensures that interventions are both relevant and effective.
2. Integrate Advanced Solutions
Leveraging technology to monitor and mitigate fatigue risks is essential for modern mining operations. Employing advanced solutions like predictive modeling tools allows for the anticipation of fatigue-related issues. These tools analyze various data points, offering insights into potential risks, which can inform strategic adjustments to shifts and tasks, keeping workers alert and operations running smoothly.
Advanced systems such as those designed to operate without connectivity—ideal for remote or underground sites—provide comprehensive monitoring capabilities. They seamlessly integrate with existing operations, delivering timely insights that help prevent fatigue-related incidents. In environments with union considerations, technology like wearable devices can ensure compliance and foster trust, maintaining a balanced approach to worker safety and privacy.
3. Build a Culture of Safety and Communication
Promoting a culture where safety and fatigue management are prioritized encourages workers to voice concerns without hesitation. Establishing open lines of communication ensures that potential fatigue issues are addressed promptly, fostering a proactive approach to safety.
Leadership is key in shaping a culture that values rest and recovery. By demonstrating a commitment to these principles, leaders set a standard for the workforce. Celebrating teams that excel in fatigue management reinforces the importance of such initiatives, fostering a work environment where everyone is committed to maintaining safety and well-being. As this culture takes root, adherence to safety measures naturally strengthens, benefiting both workers and operations.
FAQs
What are the primary causes of fatigue in mining operations?
Fatigue in mining operations often stems from the demanding nature of the work environment, which includes long shifts and heavy physical labor. Factors such as extreme temperatures and high noise levels exacerbate the situation. Additionally, the need for constant vigilance and the monotony of some tasks can lead to mental fatigue, reducing overall alertness and increasing the risk of accidents.
How can predictive technology enhance fatigue management?
Predictive tools revolutionize fatigue management by analyzing data to anticipate fatigue-related risks before they occur. These technologies evaluate variables such as workload, shift patterns, and environmental conditions to provide actionable insights. By implementing changes proactively, management can maintain a safe and efficient workplace, minimizing the likelihood of fatigue-related incidents.
What role does worker education play in managing fatigue?
Educating workers about fatigue is crucial for equipping them with the knowledge to recognize and address fatigue symptoms effectively. Training programs can focus on strategies for maintaining alertness and managing stress, encouraging an environment where discussing fatigue is normalized. This empowerment fosters a safety-first mindset and encourages collective efforts in fatigue management.
How does shift scheduling influence fatigue levels?
The structuring of shift schedules plays a pivotal role in influencing fatigue levels by either supporting or disrupting workers' natural sleep cycles. Schedules that allow for adequate rest and recovery between shifts help in maintaining energy levels. By continuously assessing and refining these schedules, operations can ensure that productivity and safety are optimized, reducing the potential for fatigue-induced errors.
As the mining industry continues to evolve, so must our approach to fatigue management. By embracing advanced technologies, fostering a culture of safety, and continuously refining our strategies, we can create a safer, healthier, and more productive work environment for all. If you're ready to take your fatigue management to the next level, book a demo to explore how Fatigue Science's predictive fatigue management software can improve safety and productivity.
Related Posts
-
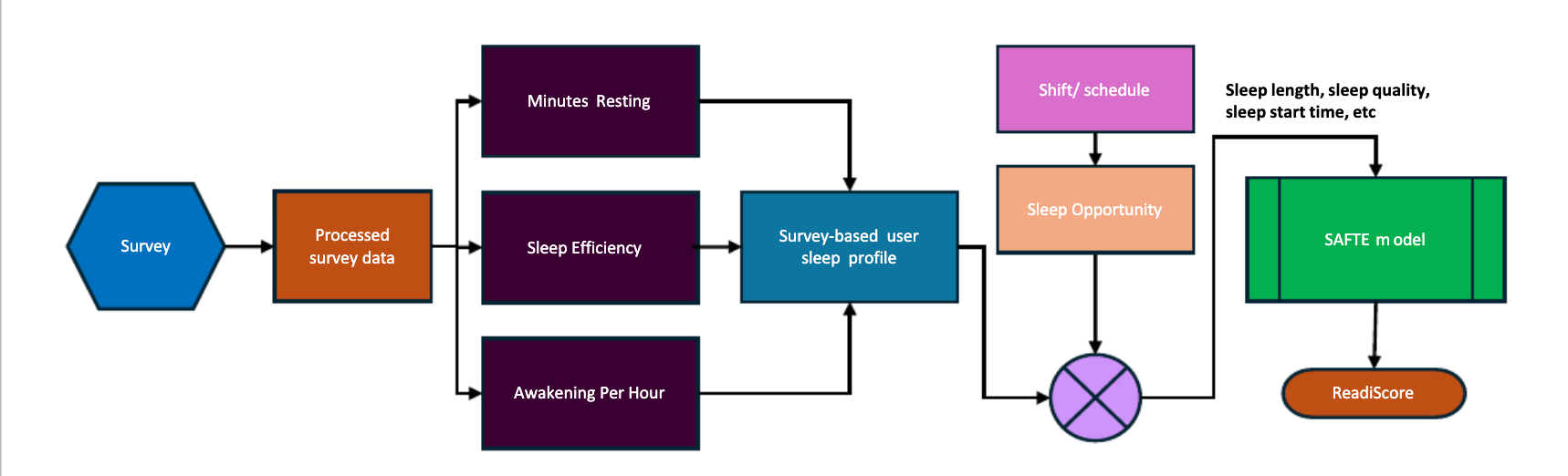
Can You Predict Fatigue Risk in Mining Without Wearables? New Research on Survey-Based Deep Learning Techniques for Measuring Fatigue Says YesFatigue is one of the biggest safety and performance risks in mining operations and other heavy industries. Workers who are tired...
-
An Interview with International Mining Magazine: A New Approach to Fatigue Management in MiningMining safety has always relied on layers of protection. What’s changing now is where those layers start.
-
Shifting From Reactive Dash Cam Safety to a Proactive Safety StrategyDash cams are now common across trucking fleets, mine sites, and people-transport operations. They help reconstruct incidents,...