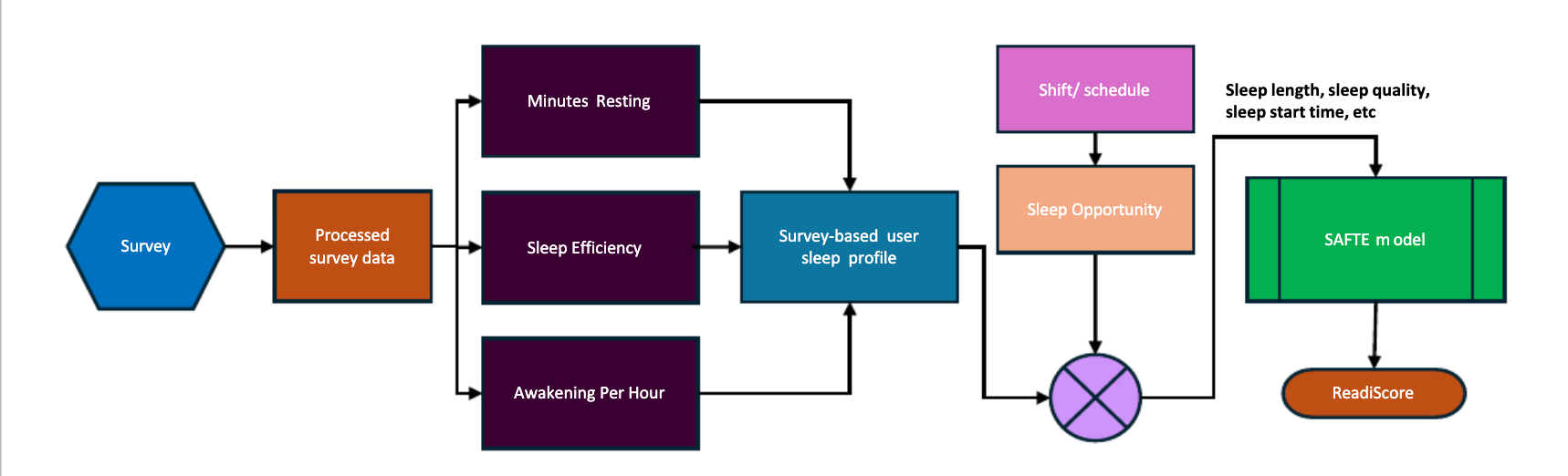
Fatigue detection tools have become increasingly crucial in the mining industry, where worker safety and operational efficiency are paramount. These tools help monitor and manage fatigue levels, reducing the risk of accidents and enhancing productivity. However, to maximize the benefits of these tools, it is essential to provide comprehensive training to staff members who will be using them -- users, supervisors, health and safety leaders, and operational personnel alike.
Effective training programs for fatigue detection tools in mining should cover a wide range of topics, from understanding the basics of fatigue to mastering the technical aspects of the tools themselves. By equipping workers with the necessary knowledge and skills, mining companies can ensure that fatigue detection technology is used to its fullest potential, contributing to a safer and more efficient work environment.
In this article, we will explore the key components of training required for staff to effectively use fatigue detection tools in mining. We will discuss the importance of developing a comprehensive training program, training supervisors on data interpretation, integrating wearable technology training, conducting safety drills and simulations, and fostering a culture of continuous learning.
What training is required for staff to effectively use fatigue detection tools in mining?
Fatigue detection tools in mining require comprehensive training programs that focus on technology usage, data interpretation, and safety protocols. This training ensures that staff can effectively utilize these tools to enhance safety and operational efficiency.
Understanding Fatigue and Its Impacts
The foundation of any fatigue management training program should be a thorough understanding of fatigue itself. Training should cover the basics of fatigue, including its causes, symptoms, and the physical and cognitive impacts on workers. Employees must also be educated on the safety implications of fatigue in mining operations, emphasizing how tiredness can lead to accidents, injuries, and reduced productivity.
Technical Training on Fatigue Detection Tools
Once staff members have a solid grasp of fatigue and its consequences, training should focus on the technical aspects of fatigue detection technology. This includes in-depth explanations of how the tools work, covering sensors, algorithms, and data interpretation. Hands-on training sessions should be conducted to familiarize staff with the software and hardware components of the tools, ensuring they can set up, monitor, and maintain the systems effectively.
- Tool Functionality: Provide comprehensive training on the inner workings of fatigue detection tools, including sensors, data collection, and analysis algorithms.
- Software and Hardware Operation: Conduct practical sessions on setting up, calibrating, and troubleshooting fatigue detection devices and software.
Data Interpretation and Response Training
Interpreting the data generated by fatigue detection tools is a critical skill for supervisors and managers. Training should focus on teaching them how to analyze and draw meaningful insights from the data. Case studies and simulations can be used to demonstrate real-world applications of fatigue data, empowering supervisors to implement proactive fatigue management strategies.
Additionally, training should include clear guidelines on how to respond when fatigue is detected. This may involve implementing rest breaks, adjusting work schedules, or reassigning tasks to ensure worker safety and maintain operational efficiency.
Safety Protocols and Procedures
Integrating fatigue detection tools into existing safety protocols and procedures is crucial. Staff should be trained on the specific actions to take when a fatigue-related risk is identified, such as initiating emergency response procedures or communicating with team members. Regular safety drills and simulations that incorporate the use of fatigue detection tools can help reinforce these protocols and ensure that staff are prepared to handle potential fatigue-related incidents.
Wearable Technology Training
As wearable fatigue detection devices become more prevalent in the mining industry, it is essential to provide specific training on their use. Staff should be trained on how to properly wear and maintain these devices, as well as how to interpret the data they generate. Emphasis should be placed on the importance of data privacy and security when using wearable technology.
Continuous Learning and Skill Development
Fatigue management training should not be a one-time event but rather an ongoing process. Encourage continuous learning by offering workshops, seminars, and e-learning modules on the latest advancements in fatigue detection technology and best practices in fatigue management. Platforms like Bucketlist can be used to recognize and reward employees who excel in these training programs, promoting a culture of continuous improvement and driving employee growth.
Tips for Enhancing Training Effectiveness
- Utilize Interactive Learning Technologies: Incorporate virtual reality and simulation tools to create immersive training experiences that better engage learners.
- Customize Training for Different Roles: Tailor training modules to the specific requirements of different job roles within the mining operation, ensuring that each employee receives relevant and targeted training.
- Collaborate with Industry Experts: Partner with fatigue management experts to provide specialized training and insights into the latest advancements in the field.
- Measure Training Impact with Data Analytics: Use data analytics to assess the effectiveness of training programs, identify areas for improvement, and track progress over time.
- Foster Peer Learning and Collaboration: Encourage knowledge sharing among employees by promoting peer-to-peer learning sessions and forums where staff can discuss their experiences and best practices in fatigue management.
By implementing comprehensive training programs that cover the technical, analytical, and procedural aspects of fatigue detection tools, mining companies can ensure that their staff are well-equipped to leverage these technologies for enhanced safety, compliance, and operational efficiency. Investing in continuous learning and skill development will help organizations stay at the forefront of fatigue management practices, contributing to a safer and more productive mining industry.
How to Implement Training for Fatigue Detection Tools
Establishing a training program for fatigue detection tools involves creating a robust structure that intertwines theoretical insights with hands-on practice. Developing a well-rounded training architecture requires pinpointing the crucial elements necessary to fully leverage fatigue management technology. This structure should seamlessly integrate both the technical functions and safety roles of fatigue detection to enable employee proficiency in diverse mining settings.
Establish a Comprehensive Training Framework
A successful training blueprint starts with a curriculum that delves into the operational intricacies of fatigue detection tools. It should encompass detailed modules on device handling, software navigation, and data management protocols. Training must also highlight how fatigue detection tools are integral to reducing risks and safeguarding workers in mining environments.
- Theoretical Insights: Offer courses that explore the physiological and psychological aspects of fatigue and their implications for worker performance in high-risk settings.
- Practical Engagement: Facilitate interactive sessions where employees actively use the tools, applying their knowledge in scenarios that mimic actual working conditions.
Focus on Technical and Safety Aspects
To maximize training efficacy, it is essential to concurrently address the technical capabilities and safety contributions of fatigue detection tools. This dual focus equips staff with the expertise needed to operate the technology while embedding safety considerations into their everyday routines.
- Technical Mastery: Host intensive workshops that cover detailed aspects of fatigue detection devices, including setup, adjustment, and problem-solving.
- Safety Collaboration: Incorporate training that aligns fatigue management strategies with existing safety measures, illustrating the direct impact on workplace safety.
Incorporate Continuous Learning and Assessment
Embedding continuous education into the training framework ensures the program remains current and adaptive to industry advancements. This involves offering ongoing learning opportunities and systematically evaluating the training's success.
- Progressive Learning Paths: Develop a series of advanced training modules and credentialing opportunities that keep employees informed about emerging trends and innovations in fatigue management.
- Systematic Evaluations: Implement regular reviews of training effectiveness to uncover knowledge or skill gaps, using insights to enhance and evolve the training approach.
By adopting a strategic approach that integrates foundational and practical training elements, mining companies can arm their workforce with the skills necessary to effectively utilize fatigue detection tools. Committing to ongoing education and embedded safety practices not only boosts operational efficiency but also nurtures a culture of safety and excellence.
1. Develop a Comprehensive Training Program
Creating a robust training program for fatigue detection tools involves formulating a detailed educational layout that empowers employees with both essential and specialized knowledge. This requires a roadmap that delves deeply into fatigue detection technology, ensuring that workers comprehend the operational mechanics necessary for maximum tool efficiency. The program should seamlessly blend conceptual understanding with hands-on application, enabling employees to apply insights practically.
Curriculum Design and Structure
The curriculum must be thoughtfully designed to encompass the entire spectrum of fatigue detection tools, from introductory concepts to advanced applications. Start with foundational modules that provide insights into the nature of fatigue, exploring its physical and mental effects on mining workers. This establishes the context for more technical training to follow.
- Core Technology Insights: Present the technological aspects of fatigue detection tools, including types of sensors, data acquisition techniques, and the principles behind fatigue monitoring systems. Detailed exploration of these components will demystify the tools, empowering employees to use them with dexterity.
- Operational Mastery: Offer precise, methodical guidelines on setting up, fine-tuning, and maintaining fatigue detection systems. This ensures that employees, regardless of their technical expertise, can operate the tools with accuracy and assurance.
Emphasizing Safety Integration and Risk Management
A pivotal part of the training program is reinforcing safety integration and fatigue risk management. This aspect of training should focus on how fatigue detection tools dovetail with comprehensive safety measures to mitigate risks and bolster the safety ethos within the mining environment.
- Integrated Safety Measures: Develop training modules that align fatigue detection with existing safety frameworks and compliance mandates. Workers should learn to incorporate tool data into safety evaluations and incident documentation, reinforcing the role of technology in promoting a safe workplace.
- Risk Management Strategies: Design targeted training on fatigue risk management, guiding employees in data interpretation and hazard identification. This involves leveraging data analytics to forecast fatigue-related risks and implementing proactive strategies to mitigate them.
By structuring the curriculum to encompass these vital areas, the training program ensures that employees are not only well-versed in the tools themselves but also in the broader implications of their use. This comprehensive approach nurtures a workforce that is proficient, safety-aware, and prepared to fully harness the benefits of fatigue detection technology.
2. Train Supervisors on Data Interpretation
Supervisors are crucial in leveraging fatigue detection systems, as their ability to analyze data effectively shapes operational strategies. To fully utilize fatigue management tools, supervisors require specialized instruction on interpreting complex data sets. This ensures they can transform data insights into strategic actions that enhance safety and operational performance.
Advanced Data Analysis Instruction
Offering comprehensive training in data analysis prepares supervisors to decode intricate fatigue metrics accurately. This instruction should emphasize understanding the diverse data inputs and outputs generated by fatigue detection systems, such as sleep cycles, alertness indicators, and physiological metrics. Mastery of these elements allows supervisors to identify patterns and connections that are not immediately obvious.
- Sophisticated Analytical Tools: Introduce supervisors to sophisticated analytical tools, enabling them to efficiently navigate large datasets and distill valuable insights. This includes training on software that aids in data visualization and recognizing patterns.
- Contextual Insight Development: Equip supervisors to place data within the broader context of operational dynamics, considering factors like shift rotations, workload demands, and environmental conditions. This comprehensive approach facilitates more nuanced data interpretations.
Practical Application through Real-world Scenarios
Bridging theoretical knowledge with practical application is best achieved through the use of real-world scenarios. These methods provide supervisors with practical experience in data interpretation, fostering the application of insights in everyday operations. By examining historical scenarios, supervisors can glean insights from past successes and failures in fatigue management, learning best practices and common challenges.
- Operational Scenario Drills: Implement drills that mimic everyday mining operations, prompting supervisors to make real-time decisions based on fatigue data. These exercises develop critical thinking and decision-making abilities, allowing supervisors to refine their strategies in a real-world context.
- Collaborative Analysis Workshops: Organize workshops where supervisors collectively examine case studies, sharing interpretations and suggested actions. This encourages knowledge exchange and cultivates an environment of continuous learning.
Empowering Supervisors with Strategic Management Skills
Empowering supervisors to manage fatigue proactively involves equipping them with the necessary skills to implement effective management strategies. Training should focus on the development of preventive measures and adaptation of strategies in response to evolving data insights.
- Strategic Planning Skills: Guide supervisors in crafting comprehensive fatigue management plans that incorporate data insights into shift planning, task distribution, and resource allocation. These plans should remain flexible, allowing for adjustments based on new data and conditions.
- Effective Communication Techniques: Train supervisors in techniques for effectively communicating fatigue data insights and management plans to stakeholders, ensuring organizational alignment and support. This promotes a unified approach to fatigue management, enhancing safety and productivity across the board.
By focusing on these key areas, training programs can elevate supervisors' proficiency in data interpretation, enabling them to make informed decisions that positively affect both employee well-being and operational efficiency. This targeted training approach not only strengthens supervisors' roles in fatigue management but also contributes to a safer, more effective mining environment.
3. Integrate Wearable Technology Training
Successfully integrating wearable technology into fatigue management involves specialized training to equip mining personnel with the skills to effectively utilize and interpret data from these devices. Training should emphasize the importance of adapting wearables to varying mining environments, enhancing both safety and productivity outcomes.
Hands-on Device Training
A key component of wearable technology training is providing employees with practical, hands-on experience. These sessions should focus on familiarizing staff with the devices' operational mechanics, ensuring they are confident in fitting and using wearables correctly. Training should replicate mining conditions to highlight the impact of environmental factors on device functionality.
- Interactive Workshops: Conduct interactive workshops that allow employees to engage with devices, practicing setup, calibration, and troubleshooting. This experiential learning method ensures they can navigate real-world scenarios effectively.
- Environmental Simulations: Implement simulations to expose employees to how wearable devices perform under various mining conditions, fostering a deeper understanding of the technology's adaptability.
Adapting Wearables to Mining Conditions
Mining environments present distinct challenges that necessitate adaptive strategies for wearable technology use. Training should provide employees with techniques to optimize device performance across different settings, ensuring reliable data collection.
- Condition-specific Modules: Offer targeted training modules that explore adjustments to device settings for factors such as temperature extremes, altitude changes, and proximity to heavy machinery. This equips employees to maintain device reliability regardless of environmental conditions.
- Scenario-based Exercises: Facilitate exercises that challenge employees to solve common wearable technology issues found in mining operations, encouraging innovative problem-solving approaches.
Prioritizing Data Privacy and Security
The integration of wearable technology demands a strong emphasis on data privacy and security. Training must highlight protocols for protecting sensitive information, focusing on secure data management practices.
- Privacy Awareness Training: Educate employees on best practices for data security, including secure data transfer and regulatory compliance standards. This ensures all personnel are aware of their responsibilities in data protection.
- Security-focused Workshops: Organize workshops that address potential security risks associated with wearable technology, empowering employees to recognize and mitigate vulnerabilities effectively.
By incorporating wearable technology training into the broader fatigue management strategy, mining companies can maximize the benefits these devices offer. This ensures that employees not only master device operation but also apply the technology strategically to improve safety and efficiency in mining operations.
4. Conduct Regular Safety Drills and Simulations
Employing regular safety drills and simulations within fatigue management training programs provides a practical framework to reinforce preparedness and operational proficiency. These exercises allow mining personnel to engage with real-world scenarios, enhancing their ability to navigate fatigue-related challenges. By integrating fatigue detection tools into these activities, companies can cultivate an environment of proactive risk management.
Designing Realistic Safety Exercises
Creating effective safety drills requires scenarios that reflect the specific challenges of mining operations, enabling employees to apply theoretical knowledge in practical situations. These exercises should not only focus on the direct application of fatigue detection tools but also incorporate decision-making and problem-solving elements.
- Tailored Scenario Development: Design drills that emulate various operational conditions, such as high-intensity shifts or adverse environmental settings, to challenge employees' adaptability and problem-solving skills.
- Inclusive Team Engagement: Facilitate drills that involve diverse roles and teams to foster collaboration and ensure comprehensive understanding across departments.
Engaging in Comprehensive Incident Simulations
Incorporating incident simulations into the training regimen encourages employees to develop coordinated response strategies. These simulations provide a safe space to practice managing fatigue-related events, offering insights into staff readiness and areas for improvement.
- Multi-layered Incident Scenarios: Develop simulations that incorporate multiple facets of fatigue management, including equipment handling, communication strategies, and emergency protocols, to build a well-rounded response capability.
- Integrated Response Planning: Align simulations with broader crisis management strategies, ensuring that fatigue detection tools are effectively woven into the safety framework.
Reviewing and Optimizing Training Outcomes
Conducting thorough evaluations post-drill allows for an assessment of training effectiveness and identification of improvement opportunities. Regular review sessions ensure the continual refinement of training strategies and reinforce a culture of excellence.
- Feedback-driven Improvement: Implement structured feedback mechanisms post-exercise, where participants can discuss their insights and suggestions. This exchange fosters a collaborative approach to enhancing safety protocols.
- Adaptive Training Enhancements: Utilize feedback and performance data to tailor training content, ensuring it remains relevant and addresses the evolving needs of the mining environment.
By embedding regular safety drills and simulations into the fatigue management training program, mining companies can ensure their workforce remains adept at managing fatigue-related risks, contributing to safer and more efficient operations.
5. Foster a Culture of Continuous Learning
Cultivating a culture of continuous learning in mining operations is vital for maintaining a workforce that is agile, informed, and capable of adapting to technological advancements. This requires a structured approach that integrates ongoing educational opportunities into the organizational framework, enabling employees to continuously enhance their skills and knowledge. By embedding continuous learning as a core value, organizations can ensure their teams remain proficient and ready to leverage cutting-edge fatigue management technologies effectively.
Dynamic Workshops and Interactive Sessions
Promoting ongoing skill development through regular workshops and interactive sessions is critical for keeping the workforce engaged with the latest industry innovations. These learning opportunities should be designed to not only impart knowledge but also to encourage active participation and collaboration among employees, fostering a shared understanding and collective growth.
- Varied Instructional Approaches: Use a combination of hands-on workshops, live demonstrations, and interactive discussions to cater to different learning preferences and maximize engagement.
- Collaborative Learning Environment: Facilitate cross-functional collaboration during these sessions to promote the exchange of ideas and enhance the overall learning experience.
Utilizing Recognition Tools for Motivation
Incorporating recognition tools to acknowledge and reward employees who excel in training initiatives serves as a powerful motivator, driving engagement and commitment to continuous improvement. Implementing a structured recognition program can serve as a catalyst for encouraging participation and excellence in training activities.
- Structured Recognition Systems: Create a comprehensive recognition framework that celebrates outstanding performance in training, reinforcing the importance of professional development and continuous learning.
- Incentive-driven Participation: Offer incentives for active participation in educational activities, such as certifications or advancement opportunities, to motivate employees to invest in their growth.
Encouraging a Growth-oriented Ethos
Fostering a growth-oriented ethos within the organization involves creating an environment where continuous learning is seen as integral to both personal and professional success. This mindset encourages employees to take charge of their development and seek out opportunities for upskilling and innovation.
- Access to Learning Resources: Provide employees with access to a wide array of learning resources, including online courses, industry conferences, and internal knowledge-sharing platforms, empowering them to pursue their development goals.
- Reflective Learning Practices: Encourage regular reflection and feedback sessions, where employees can evaluate their learning progress and set future development objectives, aligning their aspirations with organizational goals.
By instilling a culture of continuous learning, mining companies can build a workforce that is not only skilled in using fatigue detection tools but also adaptable to the evolving needs of the industry. This commitment to ongoing education ensures that employees remain engaged, knowledgeable, and prepared to contribute to safer and more efficient mining operations.
Tips on Enhancing Training Effectiveness
Enhancing the effectiveness of training programs for fatigue detection tools in mining requires a strategic approach that prioritizes engagement, relevance, and continuous improvement. By integrating modern technologies and customizing training to meet the diverse needs of employees, organizations can ensure that their workforce is equipped to optimize the use of fatigue management tools.
1. Incorporate Advanced Learning Technologies
Introducing advanced learning technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) and interactive digital platforms, can revitalize traditional training sessions. These technologies create engaging environments where employees interact with fatigue detection tools in a controlled, yet realistic setting.
- Augmented Reality Modules: Utilize AR to overlay digital information onto physical environments, helping employees visualize complex concepts in fatigue management. This method enhances comprehension and provides a unique hands-on learning experience.
- Interactive E-Learning Platforms: Develop interactive digital courses that allow employees to engage with content at their own pace, offering opportunities for exploration and self-directed learning.
2. Adapt Training for Diverse Operational Needs
Recognizing the varied operational requirements within mining operations is crucial for designing effective training. By creating adaptable training modules that address the specific challenges faced by different teams, organizations ensure that all employees receive targeted instruction that relates directly to their daily tasks.
- Adaptive Learning Paths: Construct learning paths that adjust based on individual performance, catering to employees’ unique strengths and areas for growth. This personalization fosters deeper engagement and skill mastery.
- Operationally Relevant Scenarios: Craft scenarios that reflect real-world operational challenges, giving employees the opportunity to apply their training in situations they will encounter on the job.
3. Leverage Expertise from Diverse Fields
Engaging experts from a variety of fields, including occupational health and ergonomics, can enrich training programs with multifaceted insights. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that employees gain a comprehensive understanding of fatigue management beyond their immediate work environment.
- Cross-disciplinary Workshops: Conduct workshops that bring together specialists from different fields, offering diverse perspectives on managing fatigue. These sessions provide employees with a holistic view of the factors influencing fatigue.
- Collaborative Industry Networks: Establish networks with professional organizations and universities to facilitate knowledge exchange and access to cutting-edge research and techniques.
4. Analyze Training Outcomes with Performance Metrics
Implementing a structured approach to analyze training outcomes ensures that programs remain effective and aligned with organizational goals. By utilizing performance metrics, companies can evaluate the impact of training on both individual growth and overall operational success.
- Comprehensive Feedback Systems: Deploy systems that collect detailed feedback from participants, providing insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the training program. This information is vital for making informed adjustments.
- Outcome-driven Evaluations: Focus evaluations on tangible outcomes, such as reductions in fatigue-related incidents and improvements in employee alertness, to assess the real-world impact of training initiatives.
5. Promote a Culture of Collaborative Learning
Creating a culture that values collaborative learning encourages employees to share knowledge and build on each other's experiences. This approach not only enhances individual learning but also strengthens the organization's collective capacity to manage fatigue effectively.
- Learning Communities: Establish communities of practice where employees regularly meet to discuss challenges and share solutions related to fatigue management. This peer-driven learning fosters a sense of camaraderie and shared purpose.
- Mentorship and Peer Support: Develop mentorship programs that pair experienced employees with newcomers, facilitating the transfer of knowledge and practical skills. This supportive network enhances learning and builds confidence across the workforce.
By implementing these strategies, mining companies can enhance the effectiveness of their training programs, ensuring that employees are well-equipped to utilize fatigue detection tools to their fullest potential. This commitment to excellence in training not only improves safety and productivity but also supports a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
As you embark on your journey to implement fatigue detection tools in your mining operations, remember that investing in comprehensive training is the key to unlocking the full potential of these technologies. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and empowering your workforce with the skills they need to effectively utilize fatigue management systems, you can create a safer, more productive work environment for all.
Related Posts
-
Can You Predict Fatigue Risk in Mining Without Wearables? New Research on Survey-Based Deep Learning Techniques for Measuring Fatigue Says YesFatigue is one of the biggest safety and performance risks in mining operations and other heavy industries. Workers who are tired...
-
An Interview with International Mining Magazine: A New Approach to Fatigue Management in MiningMining safety has always relied on layers of protection. What’s changing now is where those layers start.
-
Shifting From Reactive Dash Cam Safety to a Proactive Safety StrategyDash cams are now common across trucking fleets, mine sites, and people-transport operations. They help reconstruct incidents,...