Ensuring driver safety is a top priority for fleet managers and operators. Continuous fatigue monitoring has emerged as a powerful tool to detect and prevent driver fatigue, reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall road safety.
The Readi fatigue risk management system integrates with ELD systems. Download our whitepaper to learn more.
However, the implementation of these monitoring systems has raised privacy concerns among drivers and unions. Striking a balance between safety and privacy is crucial to gain acceptance and ensure the ethical deployment of fatigue monitoring technologies.
Addressing these concerns requires a comprehensive approach that involves transparent communication, robust data protection measures, and collaboration with key stakeholders. By navigating the complexities of privacy issues, organizations can harness the benefits of continuous fatigue monitoring while respecting the rights and concerns of their drivers.
What is Driver Fatigue Monitoring?
Driver fatigue monitoring is an advanced technology designed to assess a driver's alertness and detect signs of fatigue in real time. These systems may use a combination of sensors, cameras, and algorithms to analyze various parameters such as eye movement, blink rate, head position, and steering patterns.
What Is Readi, the Top Fatigue Monitoring System for Transportation Companies?
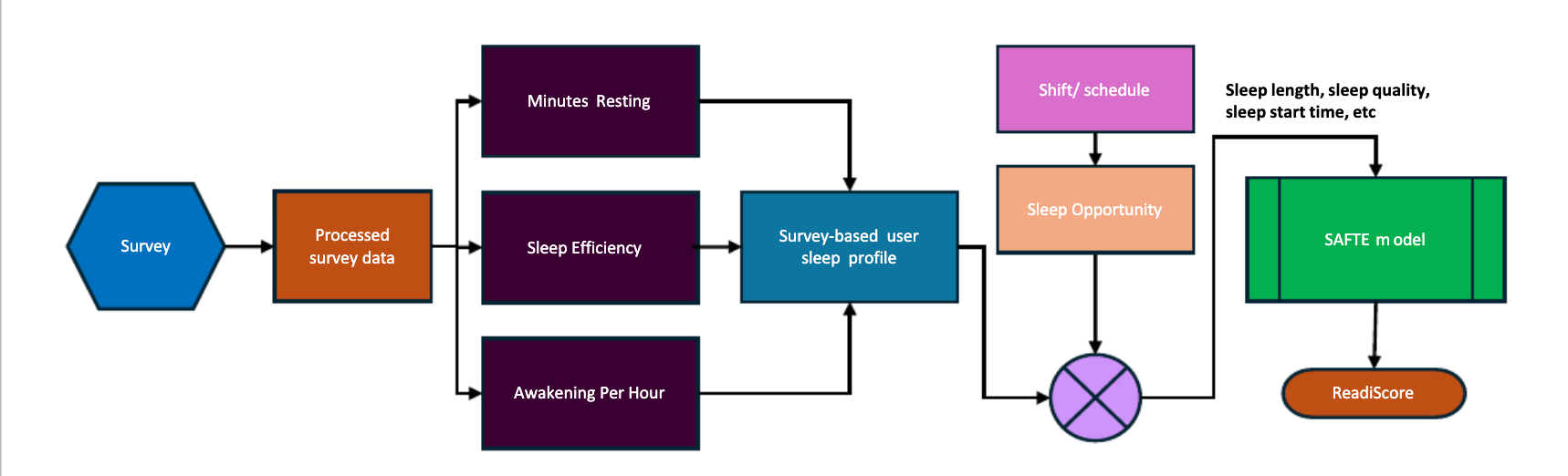
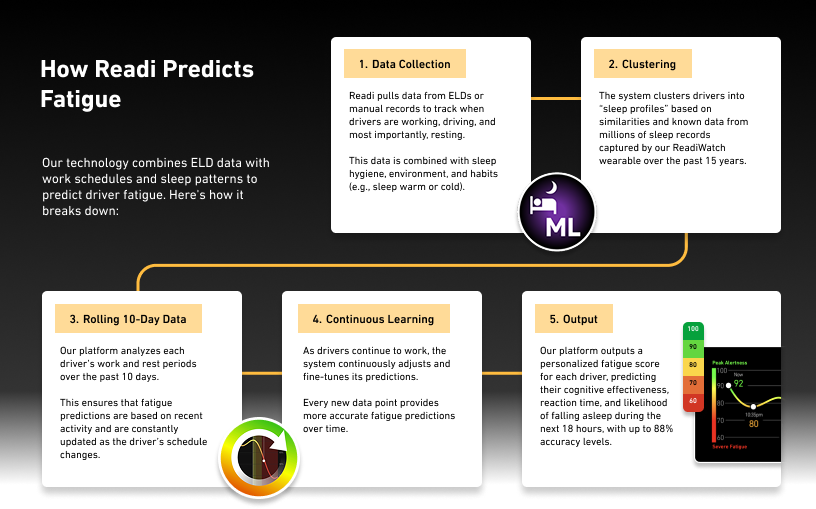
The Readi fatigue monitoring system, for example, is built on the foundation of the SAFTE Biomathematical Fatigue Model, the gold standard for fatigue risk predictions, which is actively being used by the United States Air Force and top tier industrial and transportation companies. Using the SAFTE model, Readi generates ReadiScores, which is an easy-to-understand number between 1 and 100. The ReadiScores indicate the fatigue risk level for each driver for each hour of their route to the dispatcher before the driver gets in the cab. To calculate the ReadiScore, Readi estimates the quality and quantity of a driver’s sleep using the driver’s sleep profile, past sleep opportunities and an extensive sleep database, which is validated through the SAFTE model. Readi generates ReadiScores every hour for all drivers on-duty over the next 18 hours. If a driver is determined to be at a high risk of fatigue, a non-punitive action is taken during that high-risk period.
The primary goal of driver fatigue monitoring is to enhance road safety by identifying and alerting drivers when they show signs of drowsiness or inattention. By detecting fatigue early, these systems can prompt drivers to take necessary breaks, reducing the risk of accidents caused by driver fatigue.
Continuous monitoring provides a proactive approach to fatigue management, going beyond traditional methods like hours-of-service regulations. It enables fleet managers to gain valuable insights into driver behavior and develop targeted interventions to improve safety and well-being.
However, the implementation of driver fatigue monitoring systems has raised concerns among drivers and unions regarding privacy and data protection. The collection and analysis of personal data, such as biometric information and driving patterns, can be perceived as intrusive and raise questions about how this data will be used and shared.
To address these concerns, it is essential for organizations to develop transparent policies and engage in open communication with drivers and unions.
Crucial steps for building trust and gaining acceptance for continuous fatigue monitoring include:
- Articulating the purpose of data collection
- Ensuring compliance with privacy regulations
- Implementing robust data security measures
How to Address Privacy Concerns in Driver Fatigue Monitoring
Successfully deploying driver fatigue monitoring systems necessitates an in-depth understanding of privacy issues and a dedication to tackling them head-on. These issues often focus on the potential for data misuse, surveillance concerns, and the effect on driver trust and independence.
Implement Transparent Data Policies
Building trust requires openness about data practices. Companies should craft detailed data privacy policies that specify the methods and purposes of data collection, storage, and usage. By offering drivers the ability to review their data and providing clear insights into its use, organizations can reduce anxiety over data privacy.
Transparency empowers drivers by clarifying that data collection enhances safety without infringing on privacy. Including drivers in the policy-making process ensures that their concerns are heard and addressed, fostering a culture of mutual respect and understanding.
Ensure Compliance with Privacy Regulations
Adhering to privacy legislation is crucial for the ethical use of monitoring systems. Organizations must remain updated on the legal requirements in their regions, such as those governing worker monitoring in North America. This involves consistently updating privacy policies to reflect current legal standards and frameworks.
Compliance builds a foundation of trust, as it reassures drivers that their data is managed responsibly and ethically. Routine audits and third-party evaluations can further enhance accountability and transparency, reinforcing the organization’s commitment to privacy.
Engage with Unions and Stakeholders
Proactive engagement with unions and stakeholders can alleviate privacy concerns and promote a cooperative atmosphere. Engaging unions in discussions helps address specific worries and establish terms that protect drivers’ interests. Collaborating with legal and HR teams ensures comprehensive consideration of all stakeholder concerns.
This cooperative approach minimizes potential conflicts, fostering a sense of partnership among drivers. When unions and drivers participate in decision-making, they are more likely to support monitoring systems, viewing them as collaborative safety measures rather than imposed directives.
Communicate Monitoring Policies to Drivers
Clear communication is essential for ensuring drivers understand monitoring systems’ purposes and benefits. Creating concise, accessible materials that explain systems, their advantages, and privacy measures is key. Complement these materials with training sessions to educate drivers on the role of monitoring in safety.
Training sessions offer opportunities to dispel myths and build a unified understanding of the technology. Highlighting the safety enhancements of monitoring systems can garner driver support, reinforcing that these tools are protective measures rather than punitive ones.
Balance Safety Needs with Privacy Rights
Achieving a balance between safety and privacy requires respecting driver rights while prioritizing safety. Implementing systems that anonymize data where feasible can safeguard privacy without jeopardizing safety. Reassuring drivers that monitoring systems focus on safety enhancement rather than punitive actions helps secure their trust and cooperation.
By embedding privacy into the design and implementation of monitoring systems, organizations can adeptly address privacy concerns while enhancing driver safety. This approach not only defends driver rights but also strengthens the organization’s safety culture, ensuring that safety measures are embraced and effective.
Tips on Navigating Privacy Concerns in Driver Monitoring
Effectively managing privacy issues in driver monitoring demands ongoing dedication to innovative strategies and active stakeholder engagement. Organizations can implement several key practices to address these concerns and ensure that safety and privacy coexist harmoniously.
Foster Open Dialogue
Building a culture of transparency is vital for addressing privacy concerns in driver monitoring. Establishing robust communication channels with drivers, management, and unions encourages open discussions about system implementation and operational protocols.
Regular forums or feedback sessions can help maintain a continuous exchange of ideas, fostering a cooperative environment where drivers feel involved and informed.
Regularly Evaluate and Update Policies
Keeping privacy policies current with the latest standards is essential for compliance and effectiveness. Organizations should routinely assess their data privacy practices to ensure they align with evolving regulations and technological advancements.
Engaging stakeholders in these evaluations helps tailor policies to the specific needs and expectations of drivers and unions, ensuring that privacy concerns are proactively addressed.
Provide Training and Support
Adequate training and support are crucial for helping drivers adapt to new fatigue monitoring technologies. By offering comprehensive educational programs, organizations can demystify the systems and highlight their benefits for driver safety.
These programs should focus on equipping drivers with the knowledge they need to navigate the technology confidently, thereby fostering acceptance and reducing resistance.
Showcase Benefits
Demonstrating the positive impact of monitoring systems is key to gaining support from drivers and unions. Communicating the safety enhancements and reduced fatigue-related incidents that result from these systems can help shift perceptions. Sharing success stories and data-driven outcomes reinforces the systems' value, encouraging stakeholders to embrace the technology as a beneficial tool for enhancing road safety.
Use Technology Responsibly
Choosing the right technology is paramount in addressing privacy concerns without compromising safety. Employing innovative solutions that prioritize data protection—such as AI-driven systems that predict fatigue without intrusive data collection like Readi for fleet—can maintain trust among drivers. By demonstrating a commitment to using technology ethically and responsibly, organizations can support safety objectives while respecting driver privacy.
Navigating privacy concerns in driver fatigue monitoring requires a proactive, collaborative approach that prioritizes transparency, compliance, and stakeholder engagement. By fostering open dialogue, regularly updating policies, providing comprehensive training, showcasing benefits, and using technology responsibly, organizations can strike a balance between safety and privacy.
Book a call to learn why top transportation companies use Readi for driver fatigue monitoring.
Related Posts
-
Can You Predict Fatigue Risk in Mining Without Wearables? New Research on Survey-Based Deep Learning Techniques for Measuring Fatigue Says YesFatigue is one of the biggest safety and performance risks in mining operations and other heavy industries. Workers who are tired...
-
An Interview with International Mining Magazine: A New Approach to Fatigue Management in MiningMining safety has always relied on layers of protection. What’s changing now is where those layers start.
-
Shifting From Reactive Dash Cam Safety to a Proactive Safety StrategyDash cams are now common across trucking fleets, mine sites, and people-transport operations. They help reconstruct incidents,...