Fatigue-related accidents pose a significant risk to workplace safety, particularly in industries such as transportation, mining, and construction. To address this critical issue, organizations are increasingly turning to innovative technologies that can detect and prevent fatigue before it leads to costly incidents.
Fatigue monitoring systems have emerged as a promising solution for proactively identifying signs of drowsiness and alerting individuals to take corrective action. By leveraging advanced sensors, data analytics, and real-time alerts, these systems aim to enhance safety outcomes and optimize organizational performance.
In this article, we will explore the effectiveness of fatigue monitoring systems in predicting and preventing accidents, examining their key features, real-world performance, and potential challenges. We will also discuss how organizations can successfully implement these technologies to maximize their safety benefits and mitigate fatigue-related risks.
What are fatigue monitoring systems?
Fatigue monitoring systems are sophisticated technologies designed to detect and alert individuals to signs of drowsiness and fatigue. These systems employ a combination of sensors and predictive analytics to monitor various physiological and behavioral indicators of fatigue, such as:
- Eye movements and blink patterns
- Movements
- Sleep patterns
- Heart rate variability
- Head nodding and yawning
- Steering patterns and reaction times
By continuously analyzing these data points, fatigue monitoring systems can identify the onset of fatigue before it significantly impairs performance. The primary goal of these technologies is to provide early warning of decreased alertness, enabling individuals to take proactive measures like breaks or rest periods to prevent accidents.
Fatigue monitoring systems come in various forms, from wearable devices that track physiological signals to in-vehicle cameras that monitor driver behavior. Some systems even integrate with fleet management software, allowing organizations to monitor fatigue levels across their entire workforce and identify high-risk periods or routes.
The development of fatigue monitoring technology has been driven by advancements in sensor technology, machine learning algorithms, and data analytics. As these technologies continue to evolve, fatigue monitoring systems are becoming increasingly accurate, reliable, and user-friendly, making them a valuable tool for enhancing workplace safety and preventing fatigue-related incidents.
.png?width=816&height=527&name=How%20Our%20Machine%20Learning%20Predicts%20Fatigue%20Graphic-%20816x527%20px%20(2).png)
How do fatigue monitoring systems work to prevent accidents?
Fatigue monitoring systems employ continuous evaluation of individual alertness to anticipate the onset of fatigue. These technologies harness a blend of advanced sensor networks and data analytics to capture and assess real-time physiological and behavioral indicators. By observing key metrics like eye movement patterns, sleep hygiene, sleep paterns, driving behavior, and biometric signals, these systems maintain a vigilant guard against declining alertness.
A core feature of these systems is their ability to deliver timely notifications. Upon detecting fatigue markers that indicate reduced alertness, the system activates audible or visual signals that encourage drivers to take immediate corrective measures. Options for intervention may include scheduled breaks, engaging in brief exercises, or using revitalizing techniques to counteract the effects of drowsiness. These instantaneous alerts are fundamental in mitigating accident risks by addressing fatigue before it compromises safety.

Furthermore, fatigue monitoring systems contribute to strategic safety planning by providing long-term insights. Through data analysis over extended periods, these systems can reveal trends that point to potential risk factors, such as specific times or routes prone to fatigue incidents. This information empowers organizations to implement strategic changes in work schedules or route planning, effectively minimizing future accident risks. By integrating these data-driven insights into comprehensive safety measures, organizations can enhance their risk management practices and ultimately improve their overall safety performance.
What are the key features and technologies used in effective fatigue monitoring systems?
Fatigue monitoring systems leverage an array of sophisticated technologies to create a holistic understanding of an individual's fatigue state. These systems integrate several types of sensors to collect comprehensive data. For instance, cameras are utilized to monitor subtle facial cues such as eye movement dynamics, providing insight into attention levels. Wearable devices offer another layer of data by capturing biometric signals like skin conductance, which can indicate stress or fatigue. Additionally, in-vehicle sensors track driving behavior metrics, such as lane-keeping performance, which may degrade when a driver becomes tired.
To handle and interpret the vast data streams from these technologies, fatigue monitoring systems employ advanced data analytics tools. These tools utilize predictive models that learn from historical patterns of fatigue-related data, which enhances their ability to accurately forecast fatigue levels. By adapting to new inputs, these models continuously refine their predictive capabilities, providing tailored fatigue assessments that consider individual variability in fatigue symptoms.
User interaction with fatigue monitoring systems is critical for their effectiveness. To ensure timely responses to fatigue alerts, these systems feature user-friendly interfaces that prioritize clarity and immediacy. Visual cues and auditory signals are strategically designed to capture attention without causing distraction, prompting users to take corrective actions such as rest breaks. Furthermore, safeguarding user data is paramount; therefore, these systems incorporate stringent security measures to protect sensitive information while maintaining compliance with privacy standards. This dual focus on user engagement and data protection fosters a trusted environment for the successful deployment of fatigue monitoring technologies.
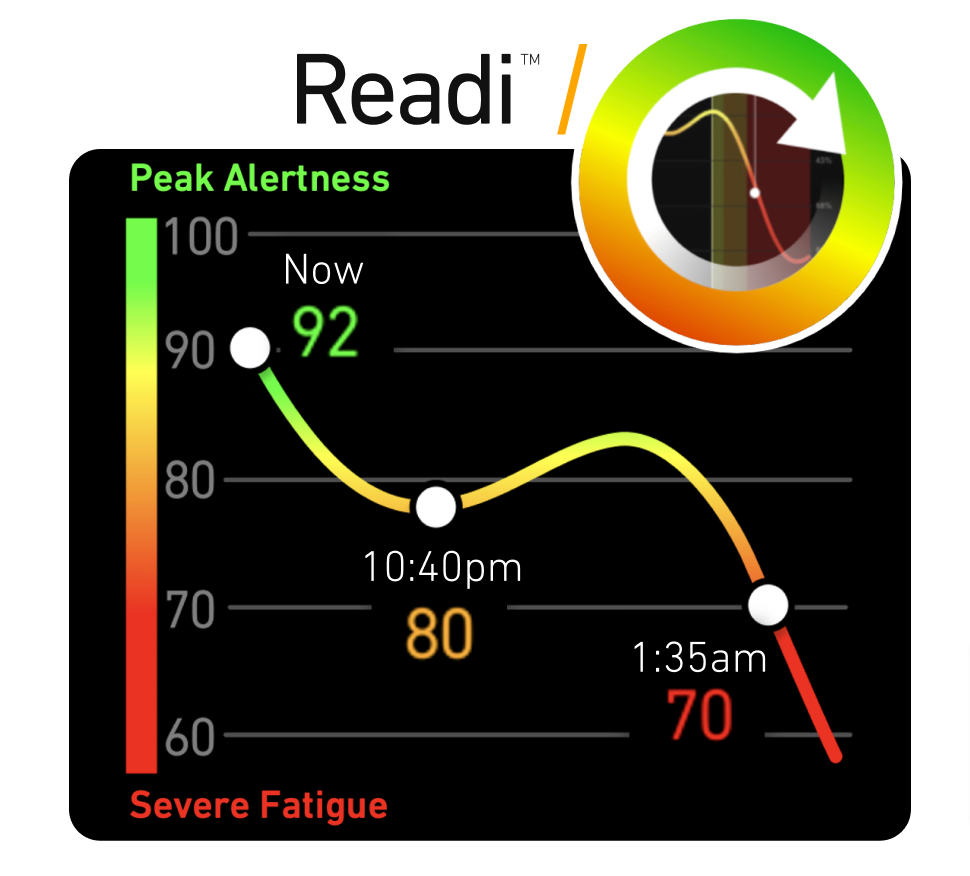
How well do fatigue monitoring systems perform in real-world settings?
Fatigue monitoring systems have shown positive outcomes in real-world applications, particularly through field studies and naturalistic driving data. Research confirms that these systems can effectively identify early signs of driver fatigue and issue prompt alerts. This capability to notify drivers before their alertness levels critically drop is integral to preventing incidents, especially in industries such as logistics and public transport where safety is paramount.
However, the performance of these systems varies based on several factors. Differences in environmental conditions, vehicle types, and driver demographics can influence system accuracy and reliability. Variabilities such as lighting, road conditions, and individual driver behaviors present challenges that may affect the consistency of these technologies. Therefore, while the potential safety benefits are significant, the effectiveness of fatigue monitoring systems can differ, requiring organizations to customize implementation strategies suited to their unique contexts.
Despite advancements, fatigue monitoring systems are not without limitations. Instances of both false alarms and missed detections highlight the necessity of incorporating these technologies within a broader safety framework. Integrating fatigue detection with comprehensive safety programs, including tailored driver education, routine checks, and strategic scheduling, can enhance the overall approach to mitigating fatigue-related risks. By doing so, organizations can maximize the efficacy of their safety initiatives and better manage risks associated with fatigue.
What are the challenges and limitations of current fatigue monitoring systems?
Fatigue monitoring systems, though advanced, face challenges due to the multifaceted nature of fatigue and diverse operational contexts. One critical challenge is tailoring detection algorithms to accommodate the unique ways fatigue manifests in individuals. This requires systems to employ adaptive models that can accurately interpret a variety of physiological and behavioral signals, enhancing precision across different user profiles. Such adaptability is often achieved through sophisticated machine learning techniques, which continue to evolve in this field.
The accuracy of fatigue monitoring systems is also affected by environmental conditions. Variations in ambient light, road surface texture, and seating ergonomics can introduce noise into sensor data, complicating accurate fatigue assessment. To address these issues, systems must integrate advanced filtering techniques capable of isolating true fatigue indicators from extraneous environmental factors. This presents both technical challenges and opportunities for innovation in sensor and algorithm development.
User confidence in fatigue monitoring systems hinges on balancing alert sensitivity with privacy considerations. Systems must avoid excessive alerts that could lead to desensitization, while providing reliable fatigue warnings. Achieving this requires carefully calibrated alert thresholds and robust privacy protections. Additionally, integrating fatigue monitoring data with broader fleet management and operational systems remains a significant hurdle. Seamless integration is crucial for leveraging fatigue data in strategic decision-making, yet it demands compatibility solutions and data management expertise. This integration is essential for developing holistic fatigue management programs that align with broader organizational safety objectives.
What advancements are needed to improve the effectiveness of fatigue monitoring systems?
Enhancing fatigue monitoring systems requires a shift towards more adaptive data frameworks. Building expansive, varied datasets is essential to reflect the diverse range of driver behaviors, vehicle environments, and operational challenges encountered across industries. These datasets should encompass a spectrum of conditions—from short urban trips to extended rural routes—to fine-tune model precision and resilience. By harnessing these enriched datasets, algorithmic learning can better identify nuanced fatigue patterns, leading to more accurate and reliable detection systems.
Introducing hybrid systems that combine multiple data types marks a significant evolution in fatigue monitoring. By integrating insights from diverse sources—such as cognitive load assessments, physiological changes like skin temperature, and dynamic vehicle feedback—these systems can construct a detailed profile of driver alertness. This convergence of diverse data points enhances the fidelity of fatigue assessments, offering a comprehensive view that single-source systems may miss. The creation of algorithms that can seamlessly interpret this complex web of data will be essential for advancing the capabilities of fatigue monitoring systems.
Progress in sensor technology also promises to elevate the effectiveness of fatigue monitoring tools. Innovations in sensors that are both discreet and capable of ongoing monitoring can significantly improve user acceptance and comfort, key factors in practical application. These advancements include non-intrusive sensors embedded in everyday items, capable of tracking physiological indicators without disrupting daily activities. By pairing these advanced sensors with algorithms that can predict fatigue risk periods, organizations can implement timely interventions. Such predictive capabilities allow for proactive measures, like recommending breaks or dynamically adjusting work hours, to curtail fatigue risks before they escalate. Through these technological advancements, fatigue monitoring systems are poised to become even more potent tools in accident prevention and safety enhancement.
How can organizations implement fatigue monitoring systems to maximize safety benefits?
Effectively deploying fatigue monitoring systems requires a coordinated approach that involves all relevant parties within the organization. It is essential to engage a diverse group of stakeholders, including drivers, supervisors, and safety consultants, in the planning and implementation phases. This collaborative effort ensures that the system reflects the practical realities of the workplace and addresses specific operational requirements. By fostering an environment of open dialogue, stakeholders can share valuable insights, allowing for a more customized and effective system design.
Incorporating fatigue monitoring systems into a holistic fatigue risk management strategy enhances their efficacy. Rather than viewing these technologies as standalone solutions, they should be integrated into broader fatigue management policies and initiatives that address the root causes of fatigue, such as optimizing shift patterns and managing workloads. By aligning technology with strategic safety objectives, organizations can effectively reduce fatigue-related hazards and improve overall safety performance. For instance, leveraging data from fatigue monitoring can inform adjustments to work schedules, thereby mitigating fatigue risks and enhancing operational efficiency.
Training and education are pivotal to the successful adoption of fatigue monitoring systems. Comprehensive training programs should be developed to ensure all users, from front-line operators to senior management, are well-versed in the system’s functionality and benefits. These programs should emphasize the importance of safety and foster an organizational culture that prioritizes alertness and well-being. Continuous learning opportunities and regular updates on system advancements will help maintain engagement and adapt to technological innovations. Additionally, incorporating feedback mechanisms allows for ongoing assessment and system enhancements, ensuring the technology remains relevant and effective.
What is the outlook for fatigue monitoring systems in accident prevention?
Organizations are increasingly aware of the significant dangers posed by driver fatigue, driving a heightened demand for robust fatigue management solutions. This awareness is leading to the adoption of cutting-edge technologies designed to detect and mitigate the risks associated with drowsy driving, further emphasizing the need for comprehensive systems that address this critical safety issue.
Technological advancements in sensor precision and data analytics are contributing to the growing effectiveness and adoption of fatigue monitoring systems. Modern sensors, coupled with sophisticated data interpretation, are enhancing the accuracy of fatigue detection, providing organizations with actionable insights. As artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms evolve, they offer more refined predictive capabilities, helping to preemptively address potential fatigue-related incidents.
By integrating fatigue monitoring data into larger safety and operational frameworks, organizations can create cohesive strategies that address various risk factors. Incorporating these insights into holistic driver safety platforms, insurance models, and urban transportation systems enhances overall safety measures. This integration not only fortifies accident prevention strategies but also exemplifies the potential of fatigue monitoring systems to significantly reduce fatigue-related incidents on a global scale.
Related Posts
-
How to Navigate Privacy Concerns in Driver Fatigue Monitoring for DriversEnsuring driver safety is a top priority for fleet managers and operators. Continuous fatigue monitoring has emerged as a...
-
Training Strategies for Implementing Fatigue Detection in MiningFatigue detection tools have become increasingly crucial in the mining industry, where worker safety and operational efficiency...
-
What are the costs associated with deploying fatigue detection technologies?Fatigue detection technologies have emerged as a critical tool for organizations looking to enhance safety, productivity, and...




